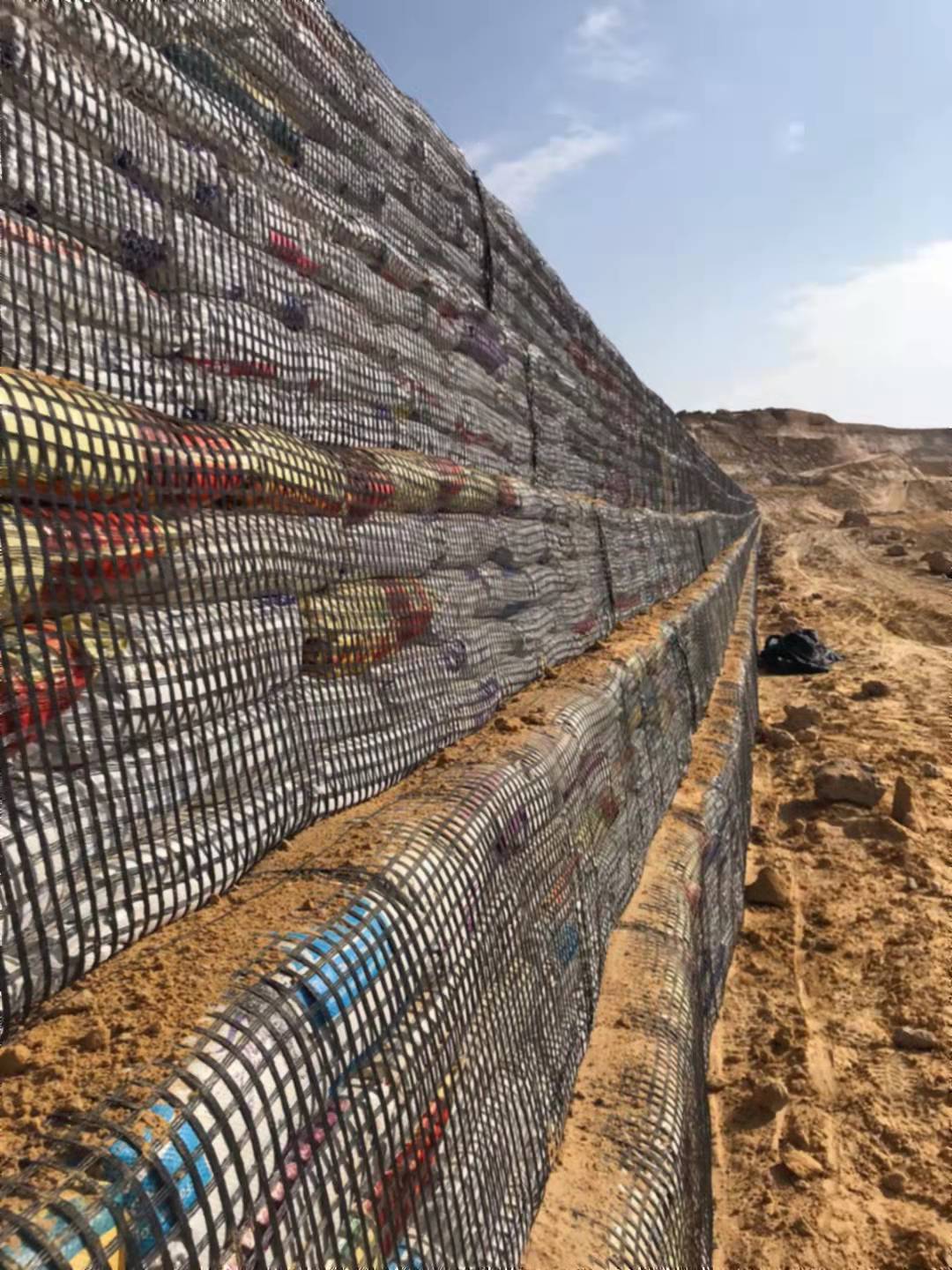
Key Features of 2D Geonet:
- Material: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP), providing excellent chemical resistance and durability.
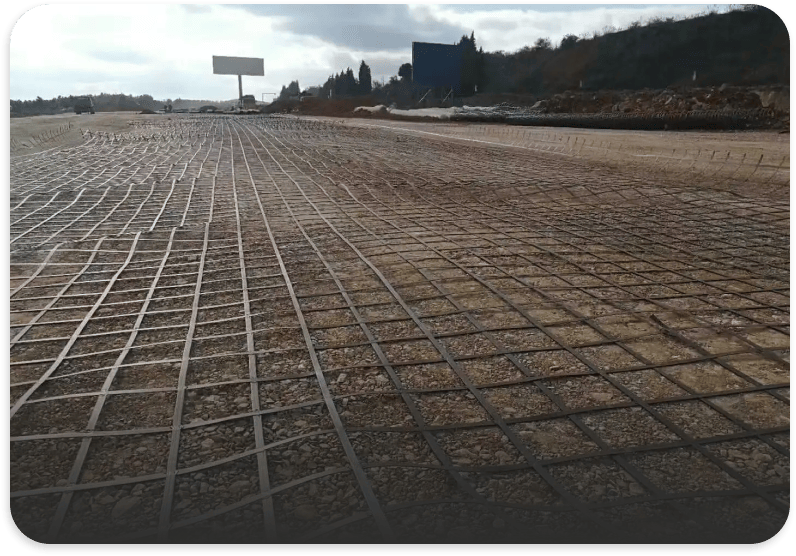
- Structure: Two-dimensional grid pattern with intersecting ribs, creating a network of channels for efficient drainage.
- Thickness: Varies depending on the application, generally ranging from a few millimeters to over a centimeter.
- Permeability: High flow capacity for both liquids and gases.
Applications:
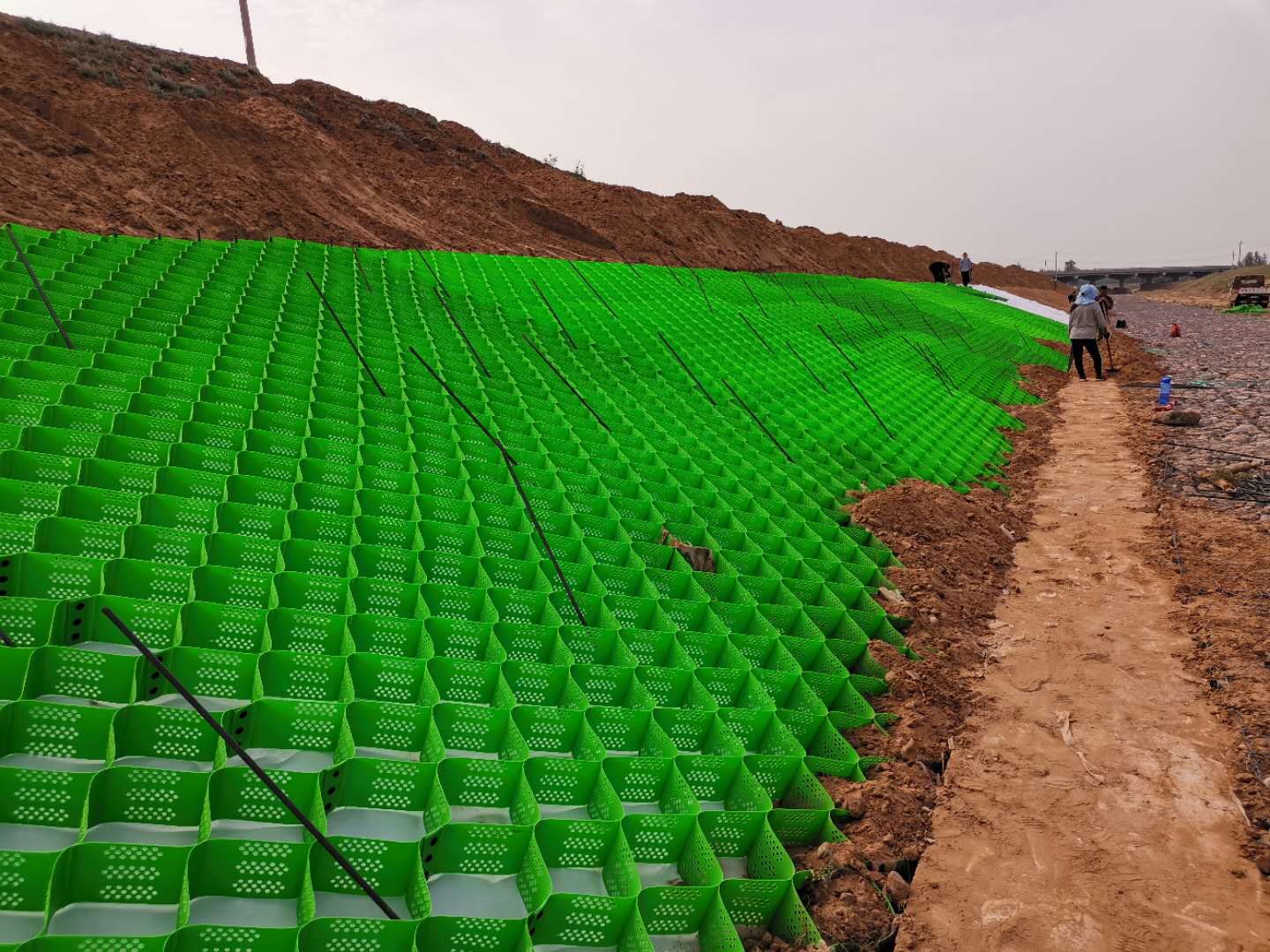
- Landfill Liners and Covers: Used as a drainage layer to manage leachate and gas flow, preventing contamination of surrounding soil and groundwater.
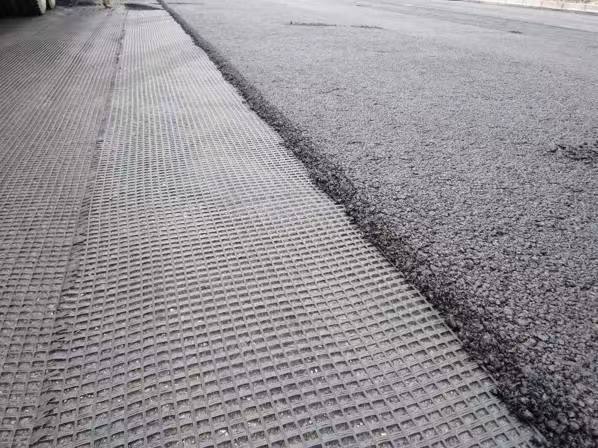
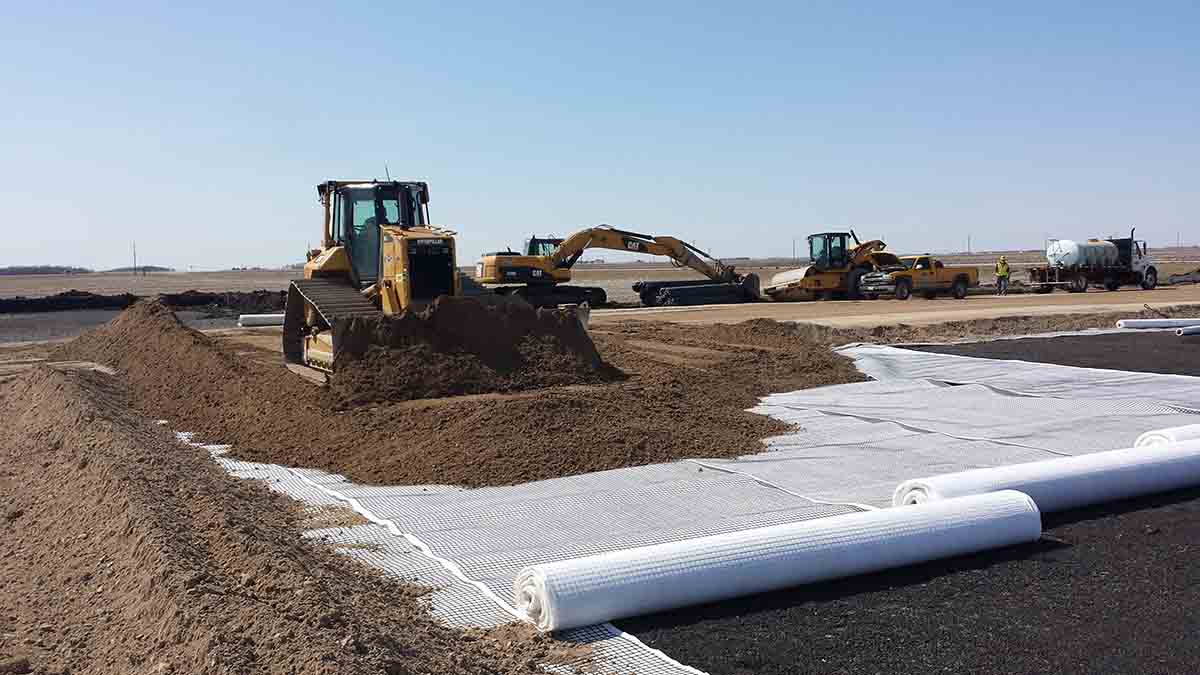
- Road and Railway Construction: Placed under roadways and railways to enhance drainage, reduce pore water pressure, and prevent subgrade saturation.
- Retaining Walls: Installed behind retaining walls to relieve hydrostatic pressure and manage water flow.
- Tunnel Drainage: Applied in tunnel linings to control water infiltration and protect the structural integrity of the tunnel.
- Green Roofs: Used in green roof systems to provide drainage and prevent waterlogging.
Advantages:
- Efficient Drainage: High flow capacity ensures effective management of water and gas, reducing hydrostatic pressure and preventing buildup.
- Durability: Resistant to chemicals, UV radiation, and biological degradation, ensuring long-term performance.
- Easy Installation: Lightweight and flexible, making it easy to handle and install in various configurations.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for traditional drainage materials and maintenance, lowering overall project costs.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications in different environmental and engineering contexts.
Manufacturing Standards
- Raw Material Quality
- Polypropylene (PP): High-quality virgin or recycled PP resins are used, with additives to enhance UV resistance, chemical stability, and durability.
- Standards Compliance: The raw materials should comply with international standards such as ASTM, ISO, or EN to ensure consistency and performance.
- Extrusion Process
- Extrusion: PP geonets are typically manufactured using an extrusion process where molten PP is passed through a die to form a net-like structure.
- Temperature Control: Precise control of extrusion temperature is essential to maintain the physical and mechanical properties of the geonet.
- Die Design: The die design is critical for ensuring uniform aperture size, thickness, and overall dimensional stability.
- Cooling and Stretching
- Cooling: The extruded geonet is rapidly cooled to set the material properties.
- Stretching: The geonet may undergo a stretching process to orient the polymer molecules, enhancing tensile strength and stiffness.
- Aperture Size and Shape
- Uniformity: Consistent aperture size and shape are crucial for the performance of the geonet in filtration and drainage applications.
- Customization: Aperture size and shape can be customized based on specific application requirements.
Quality Control Measures
- Raw Material Testing
- Resin Quality: Testing the quality and properties of the PP resin, including melt flow index (MFI), density, and contamination levels.
- Additives: Ensuring the correct type and amount of UV stabilizers, antioxidants, and other additives are incorporated.
- In-Process Monitoring
- Extrusion Parameters: Continuous monitoring of extrusion parameters such as temperature, pressure, and extrusion speed.
- Aperture Size and Shape: Real-time measurement and control of aperture size and shape using optical or laser-based systems.
- Mechanical Testing
- Tensile Strength: Testing the tensile strength of the geonet to ensure it meets the required specifications.
- Elongation: Measuring the elongation at break to assess the flexibility and ductility of the geonet.
- Tear Resistance: Evaluating the tear resistance to ensure durability under stress conditions.
- Dimensional Stability
- Thickness and Weight: Regular measurement of thickness and weight to maintain consistency.
- Dimensional Checks: Ensuring the geonet dimensions (width, length, and aperture size) are within specified tolerances.
- Environmental Resistance Testing
- UV Resistance: Accelerated weathering tests to assess the UV stability of the geonet.
- Chemical Resistance: Testing the resistance of the geonet to chemicals commonly encountered in the application environment.
- Thermal Stability: Evaluating the performance of the geonet under varying temperature conditions.
- Quality Assurance Procedures
- ISO Certification: Adherence to ISO 9001 quality management systems to ensure consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
- Batch Testing: Conducting batch-wise testing to ensure each production run meets the required standards.
- Traceability: Maintaining detailed records of raw materials, production parameters, and quality control results for traceability.
- Final Product Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Checking for visual defects such as surface irregularities, holes, or tears.
- Physical Testing: Final round of mechanical testing to verify compliance with specifications.
- Packaging and Labeling: Ensuring proper packaging to prevent damage during transportation and clear labeling for identification.