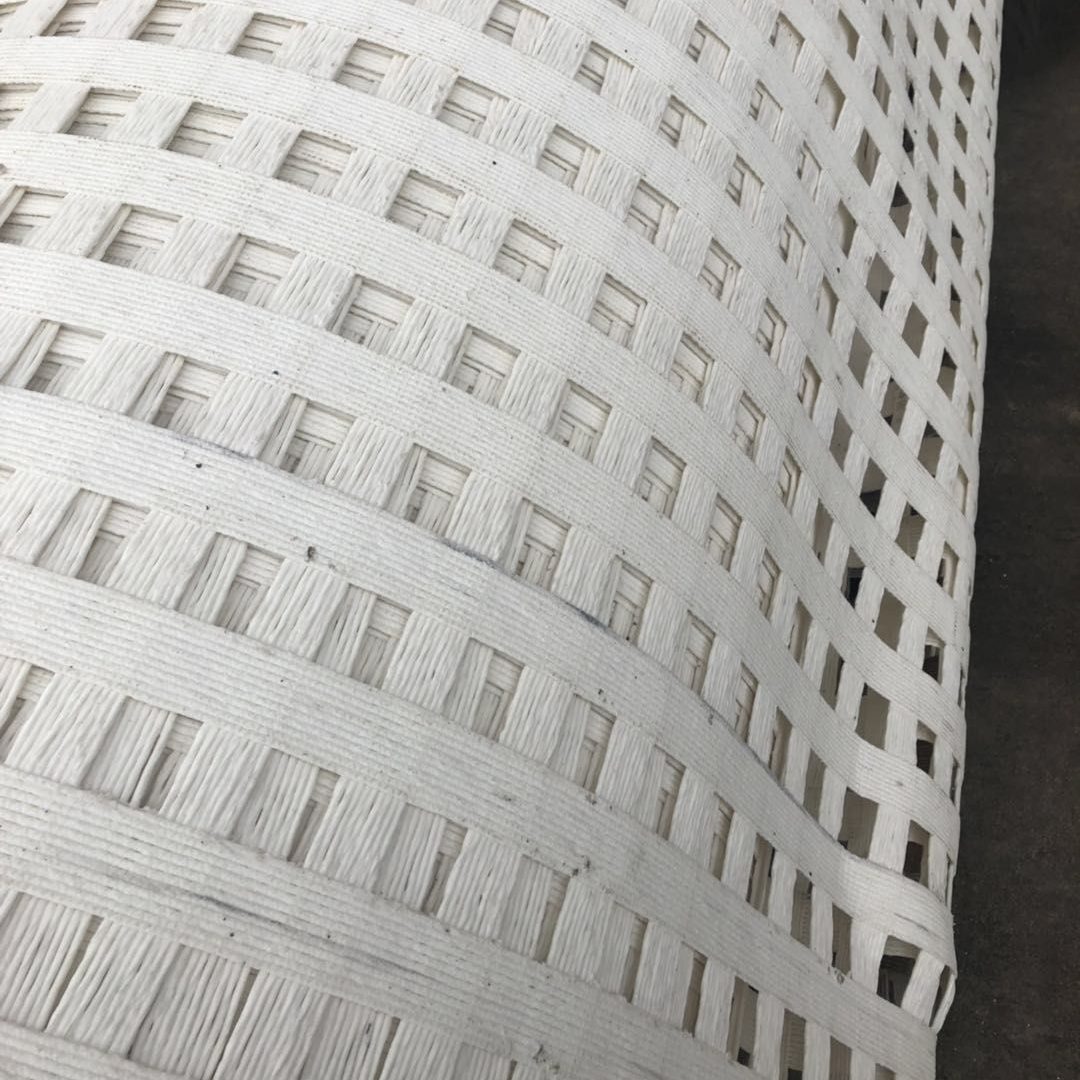
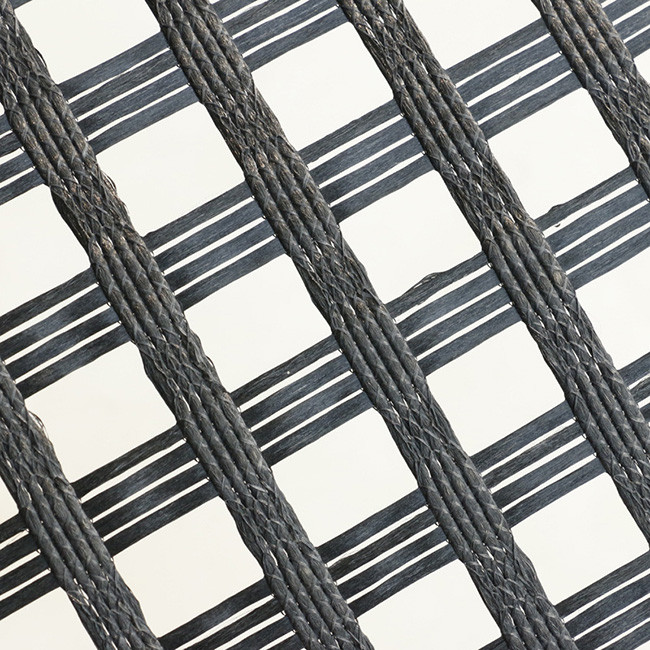
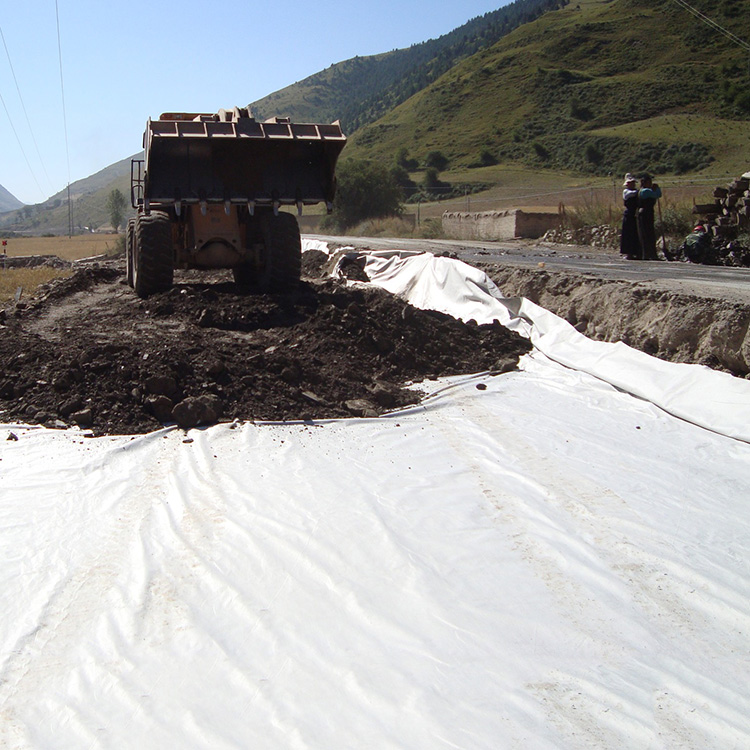
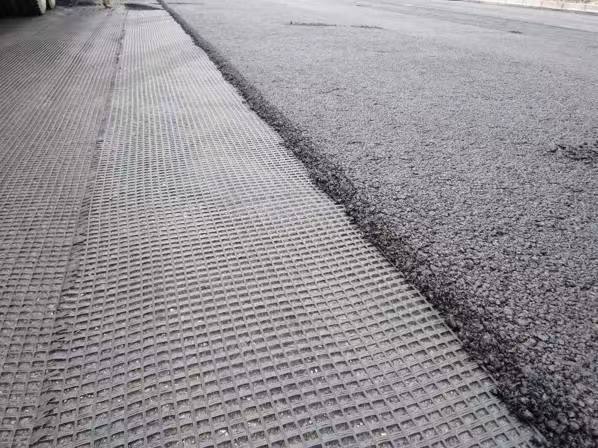
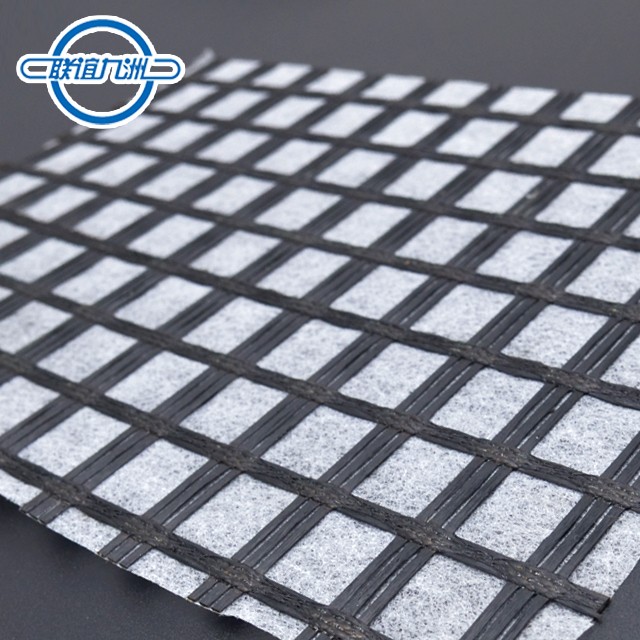
Fiberglass geogrids are widely used in pavement and road construction due to their excellent tensile strength and minimal elongation. When combined with a nonwoven fabric and bonded with glue, the composite material enhances the overall performance, providing additional benefits like improved stress absorption and moisture control.
Benefits of Composite Material
- Enhanced Load Distribution: The combination of fiberglass geogrid and nonwoven fabric distributes loads more effectively, reducing stress concentrations and preventing cracks.
- Moisture Barrier: The nonwoven fabric acts as a barrier to moisture, preventing water from penetrating the pavement layers and reducing the risk of pavement damage.
- Improved Stress Absorption: The composite material can better absorb and distribute stress, increasing the lifespan of the pavement.
- Erosion Control: The nonwoven fabric helps prevent soil erosion, enhancing the stability of the underlying soil.
Applications
- Road and Pavement Construction: Used for reinforcing asphalt layers and preventing reflective cracking.
- Railway Construction: Provides stabilization and reinforcement for railway tracks.
- Bridge Deck Reinforcement: Enhances the durability and lifespan of bridge decks.
- Airport Runways and Taxiways: Ensures long-lasting performance under heavy traffic loads.
- Parking Lots and Driveways: Provides reinforcement and reduces maintenance needs.
Performance Characteristics
Fiberglass Geogrid:
- Tensile Strength: Provides high tensile strength and stiffness with minimal elongation, typically around 100 kN/m or higher.
- Load Distribution: Effectively distributes loads and reinforces the soil or pavement structure.
- Durability: Resistant to chemical exposure and environmental conditions, especially when coated.
Fiberglass Geogrid Composite:
- Enhanced Tensile Strength: The addition of the nonwoven fabric layer can improve the overall tensile strength and durability.
- Moisture Barrier: The nonwoven fabric layer acts as a moisture barrier, preventing water penetration and reducing the risk of pavement damage.
- Improved Stress Absorption: The composite material can better absorb and distribute stress, increasing the lifespan of the reinforced structure.
Installation and Handling
Fiberglass Geogrid:
- Easy to Handle: Lightweight and flexible, making it easy to transport and install.
- Simple Installation: Requires proper surface preparation and alignment but is straightforward to install.
Fiberglass Geogrid Composite:
- More Complex Handling: Slightly heavier and less flexible due to the additional nonwoven fabric layer, but still relatively easy to handle.
- Surface Preparation: Requires similar surface preparation as fiberglass geogrid, but additional care may be needed to ensure proper bonding and placement of the composite material.
Cost Considerations
Fiberglass Geogrid:
- Cost-Effective: Generally more cost-effective due to the simpler manufacturing process and materials used.
Fiberglass Geogrid Composite:
- Higher Cost: Typically more expensive due to the additional nonwoven fabric layer and the bonding process, but offers enhanced performance benefits.
Summary of Key Differences:
| Feature | Fiberglass Geogrid | Fiberglass Geogrid Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fiberglass strands woven into a grid | Fiberglass geogrid combined with nonwoven fabric |
| Structure | Regular square or rectangular apertures | Grid with additional fabric layer |
| Tensile Strength | High, around 100 kN/m or higher | Enhanced tensile strength |
| Moisture Barrier | No | Yes, due to nonwoven fabric layer |
| Stress Absorption | Good | Improved stress absorption |
| Load Distribution | Effective | Enhanced due to composite structure |
| Applications | Roads, slopes, railways, retaining walls | Enhanced road applications, bridge decks, airport runways, erosion control |
| Installation | Easy to handle and install | Slightly more complex but still manageable |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Higher cost due to additional material |
Using fiberglass geogrid for asphalt reinforcement
Resistance to Environmental Factors
- Chemical Resistance: Fiberglass geogrid is resistant to chemicals commonly found in the pavement environment, such as oils, fuels, and de-icing salts.
- UV Resistance: Coated with a protective layer, fiberglass geogrid offers good resistance to UV radiation, preventing degradation when exposed to sunlight.
Thermal Stability
- Temperature Range: Fiberglass geogrid maintains its structural integrity over a wide range of temperatures, from extreme cold to high heat, making it suitable for various climates.
- Thermal Compatibility: The thermal expansion properties of fiberglass closely match those of asphalt, reducing the risk of differential movement and associated cracking.
Ease of Installation
- Lightweight and Flexible: Fiberglass geogrid is lightweight and easy to handle, making installation straightforward and efficient.
- Self-Adhesive Option: Self-adhesive fiberglass geogrid further simplifies installation, ensuring good adhesion to the underlying surface and reducing the need for additional bonding agents.
Cost-Effective Solution
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in fiberglass geogrid may be higher than other reinforcement methods, the extended pavement life and reduced maintenance needs result in significant long-term cost savings.
- Reduced Overlay Thickness: The use of fiberglass geogrid can allow for a reduction in the thickness of asphalt overlays without compromising performance, leading to material cost savings.