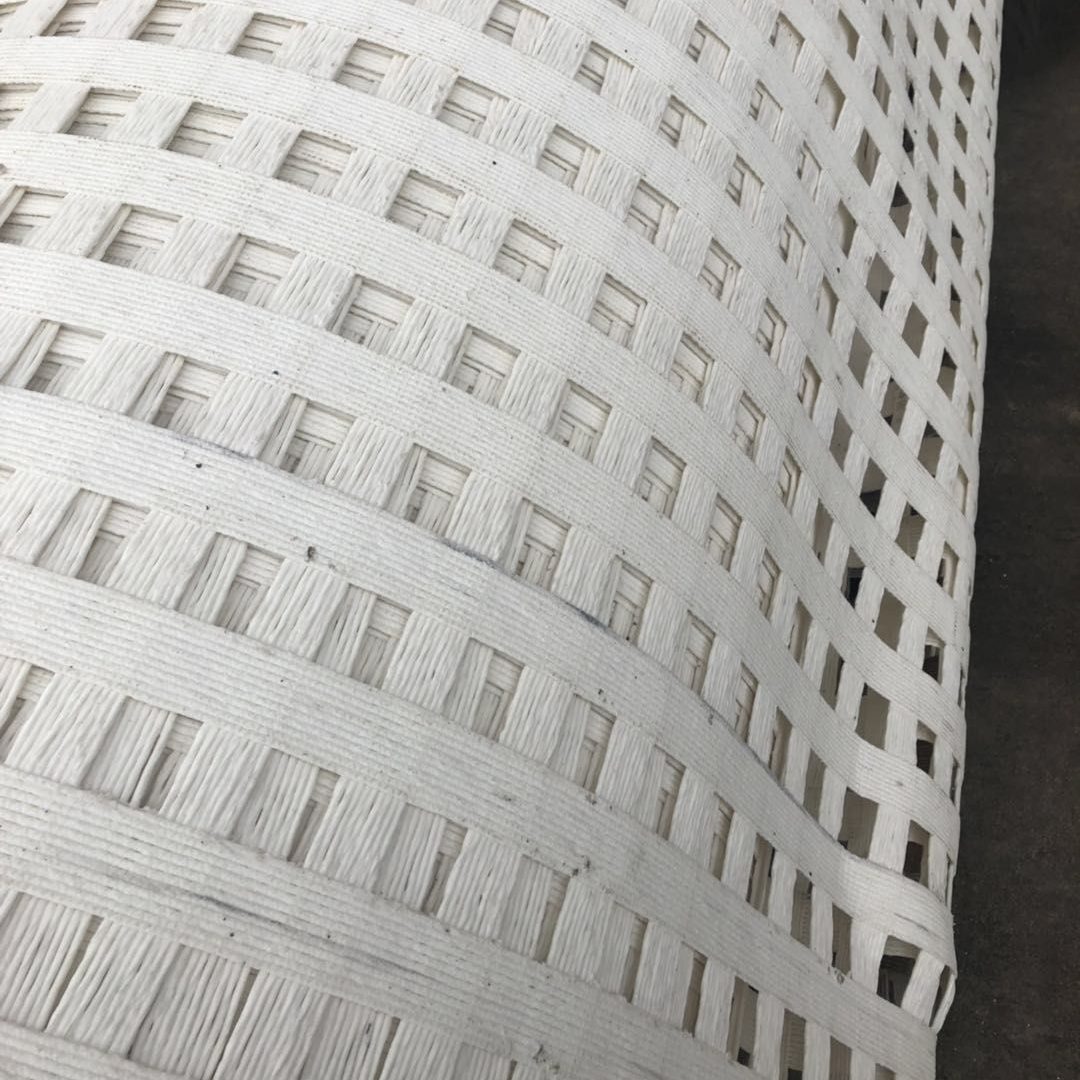
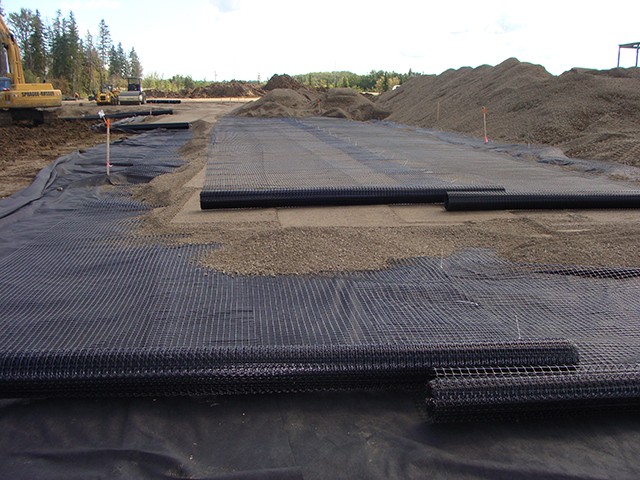
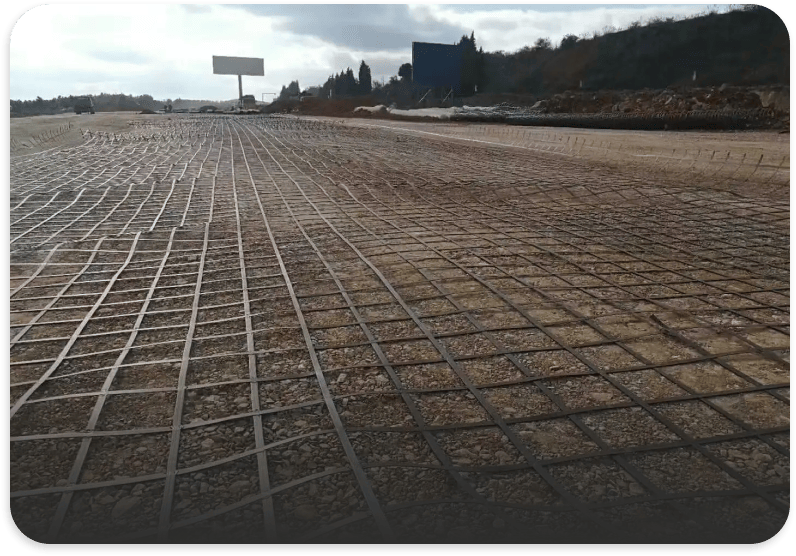
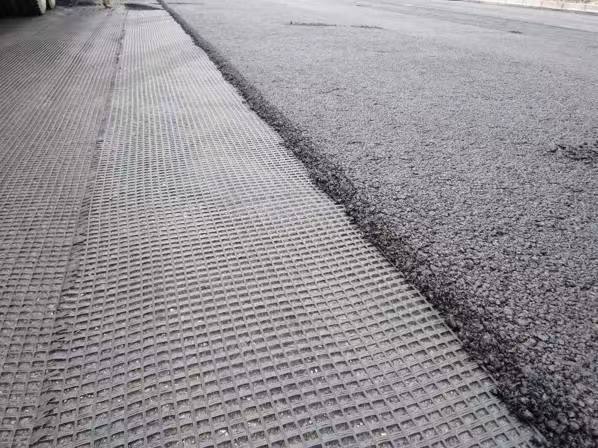
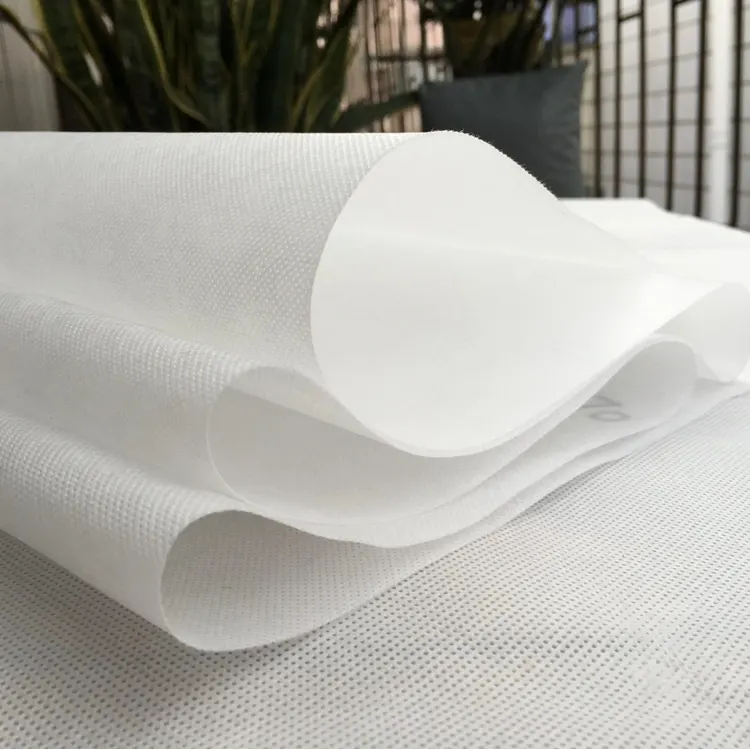
Polyester spunbond nonwoven fabric is a versatile material made from polyester fibers using the spunbond process. This type of fabric is known for its strength, durability, and various functional properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Here’s an overview of polyester spunbond nonwoven fabric:
Characteristics:
- Strength and Durability: It is robust and resistant to wear and tear, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Uniformity: The spunbond process creates a uniform fabric with consistent quality and appearance.
- Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to many chemicals, including acids and solvents, which enhances its suitability for industrial use.
- Thermal Stability: It can withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming.
- Lightweight: Despite its strength, it remains lightweight and easy to handle.
- Water Resistance: It can be engineered to be water-resistant or waterproof.
- Air Permeability: Depending on the application, it can be designed to allow air flow while blocking liquids and particles.
- Recyclability: Polyester spunbond fabric is recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Uses:
- Medical and Hygiene Products: Used in the production of disposable medical gowns, masks, caps, and other hygiene products due to its sterility and protective properties.
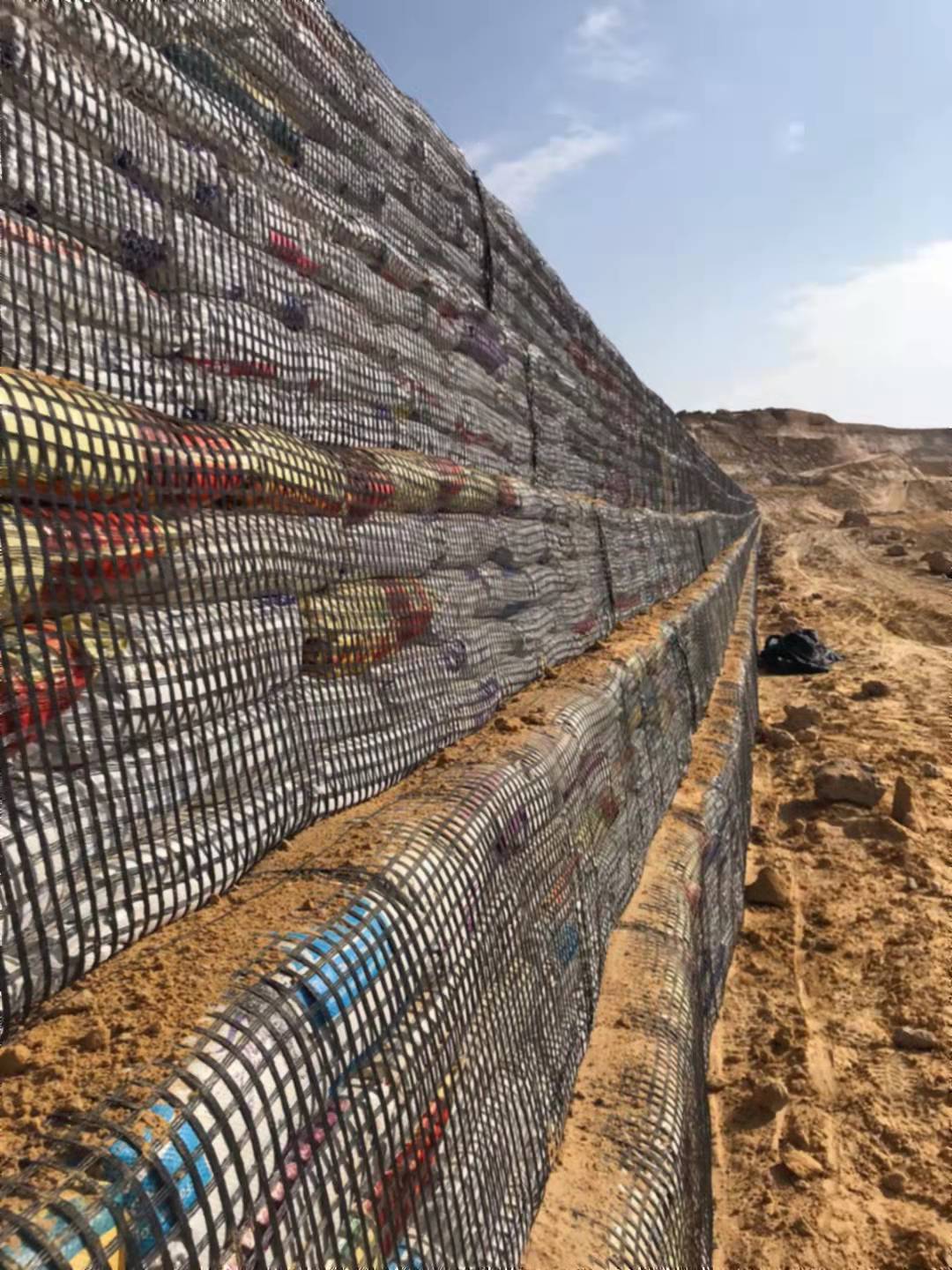
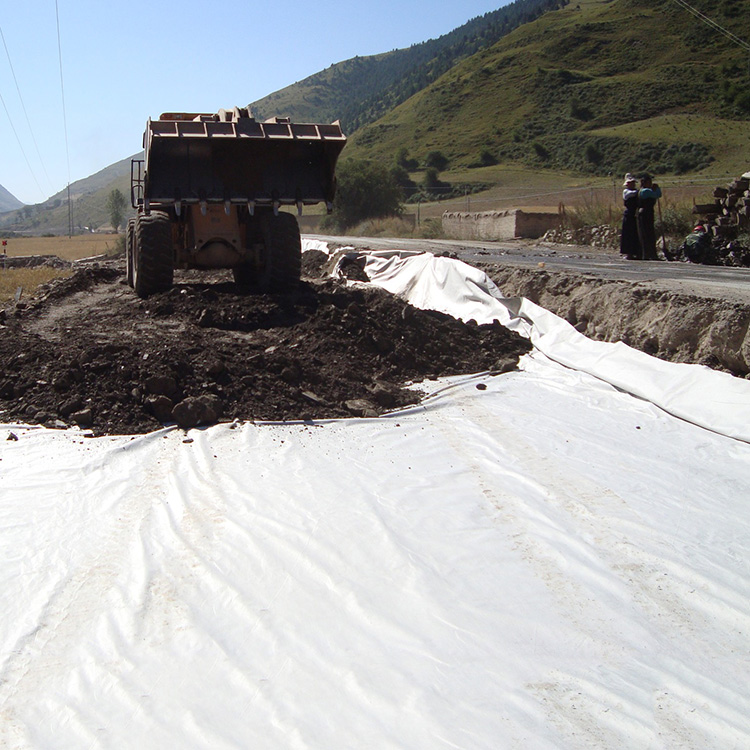
- Geotextiles: Employed in construction and civil engineering for soil stabilization, erosion control, and drainage systems.
- Agriculture: Used for crop protection, weed control, and as a barrier for soil moisture retention.
- Automotive Industry: Used for insulation, soundproofing, and interior linings in vehicles.
- Packaging: Utilized in various packaging solutions due to its durability and resistance to punctures.
- Furniture and Bedding: Used in mattress covers, furniture linings, and other home textiles.
- Filtration: Employed in air and liquid filtration systems due to its ability to trap particles while allowing fluid flow.
Manufacturing Process:
The spunbond process for making polyester nonwoven fabric involves several steps:
- Polymer Melting: Polyester polymer is melted to form a viscous liquid.
- Extrusion: The melted polymer is extruded through spinnerets to create continuous filaments.
- Web Formation: The filaments are laid down in a random or oriented pattern on a conveyor belt to form a web.
- Bonding: The web is bonded together using heat, pressure, or ultrasonic methods to create a cohesive fabric.
- Finishing: The fabric undergoes various finishing processes, such as calendaring, coating, or laminating, to enhance its properties and performance.
Quality Control Measures
- Raw Material Inspection:
- PET Resin: Quality checks are performed on the PET resin used in the production of spunbond nonwoven fabric. This includes assessing characteristics such as melt flow index, intrinsic viscosity, and purity to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- Production Process Monitoring:
- Process Parameters: Continuous monitoring of process parameters during extrusion and spinning ensures consistent fiber quality and uniformity.
- Surface Inspection: Visual inspection of the fabric surface to detect defects such as holes, tears, or irregularities that could affect performance.
- Dimensional Stability:
- Measurement of fabric dimensions and weight to ensure consistency and adherence to product specifications.
Testing Methods
- Mechanical Properties:
- Tensile Strength: Testing the fabric’s resistance to tensile forces to ensure it meets strength requirements for intended applications.
- Elongation: Measurement of the fabric’s ability to stretch under tensile load, ensuring it can withstand deformation without failure.
- Physical Properties:
- Thickness: Measurement of fabric thickness using standardized methods to ensure uniformity.
- Density: Determination of fabric density to verify consistency and coverage.
- Durability and Performance:
- Abrasion Resistance: Testing resistance to abrasion to assess durability and suitability for applications requiring mechanical strength.
- Puncture Resistance: Evaluation of the fabric’s ability to withstand punctures, important for applications where protection against sharp objects is crucial.
- Chemical and Environmental Resistance:
- UV Stability: Exposure to ultraviolet light to assess resistance to degradation and discoloration over time.
- Chemical Resistance: Testing fabric response to various chemicals to ensure compatibility with environmental conditions and applications.
Compliance and Certification
PET spunbond nonwoven fabric manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and regional regulatory requirements. Certification ensures that the fabric meets quality, performance, and safety standards for specific applications in industries such as construction, automotive, agriculture, and medical.