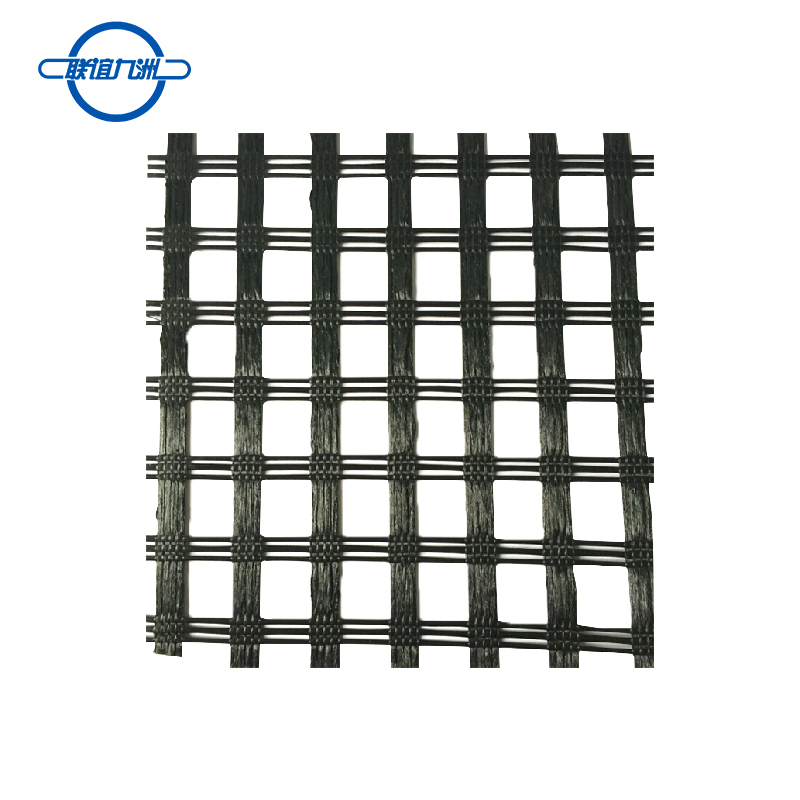
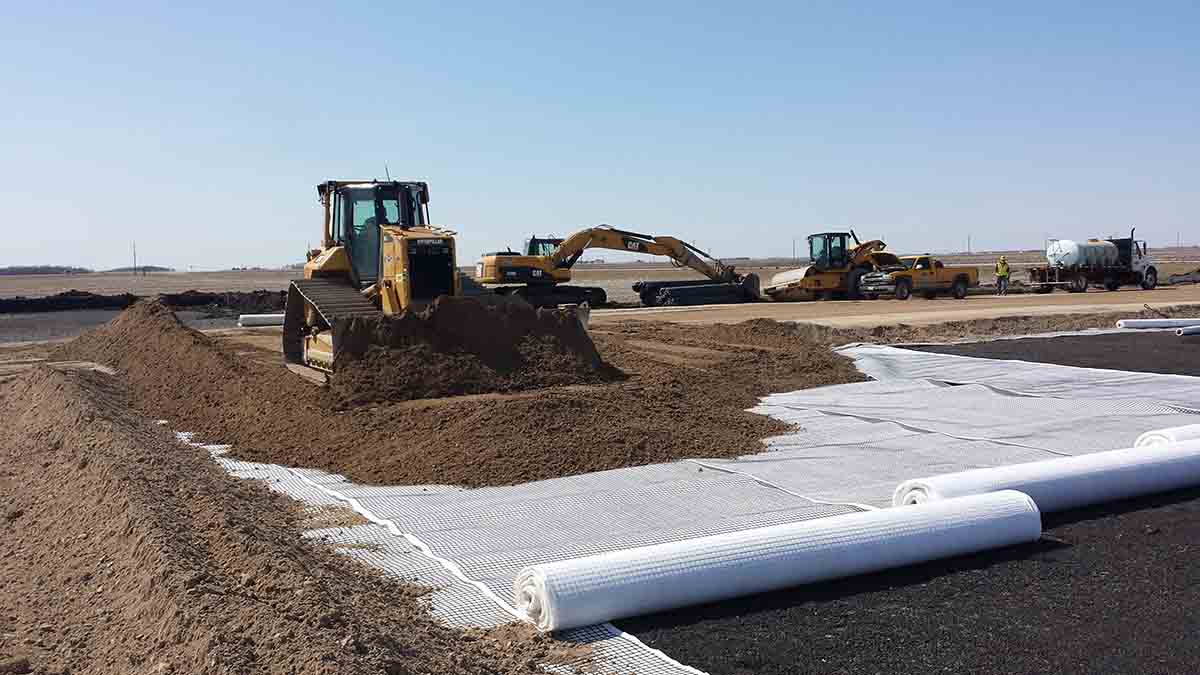
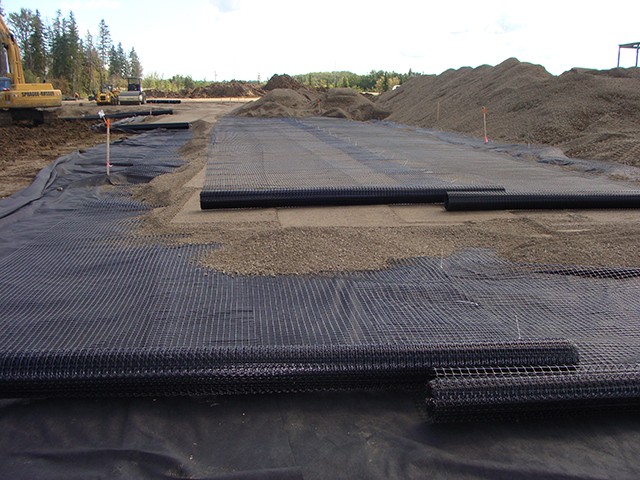
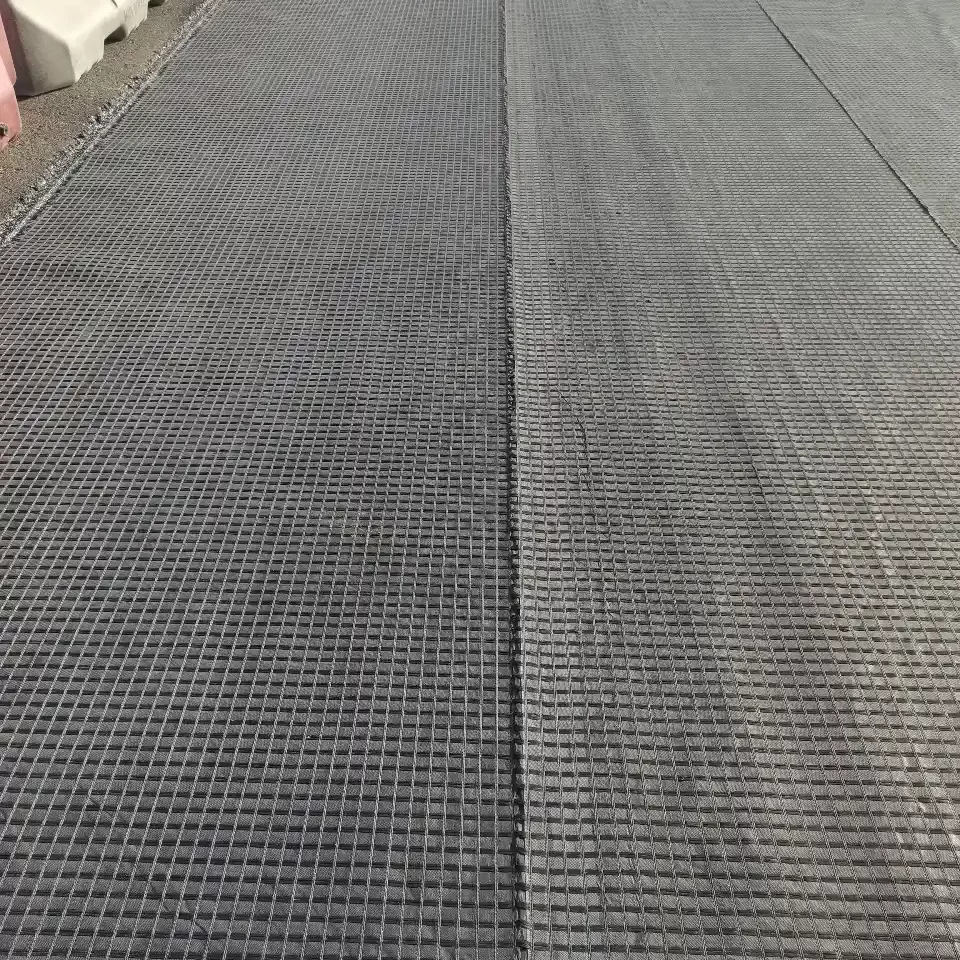
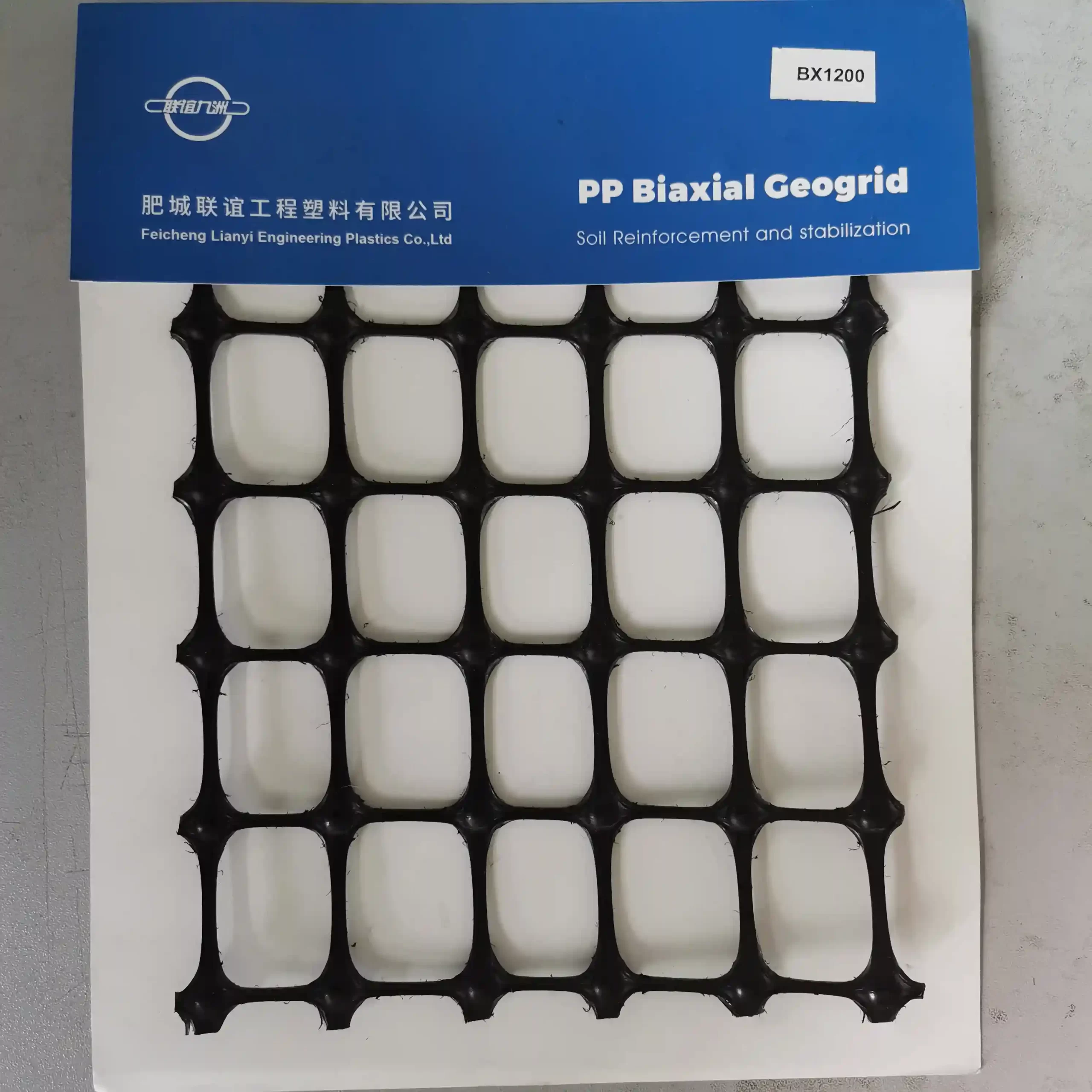
PET WELDED GEOGRID
Advantages of PET Welded Geogrids:
- High Tensile Strength: Provides significant reinforcement to the soil, capable of supporting heavy loads and preventing soil displacement.
- Low Elongation: Ensures minimal deformation under load, maintaining structural integrity and stability over time.
- Durability: Resistant to chemicals, UV degradation, and biological factors, ensuring a long service life.
- Load Distribution: Efficiently distributes loads over a larger area, reducing stress on the underlying soil and preventing subsidence.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for extensive ground preparation and additional materials, leading to cost savings in construction projects.
Applications:
- Road Construction: Used to reinforce road bases and subbases, improving load-bearing capacity and preventing rutting and cracking.
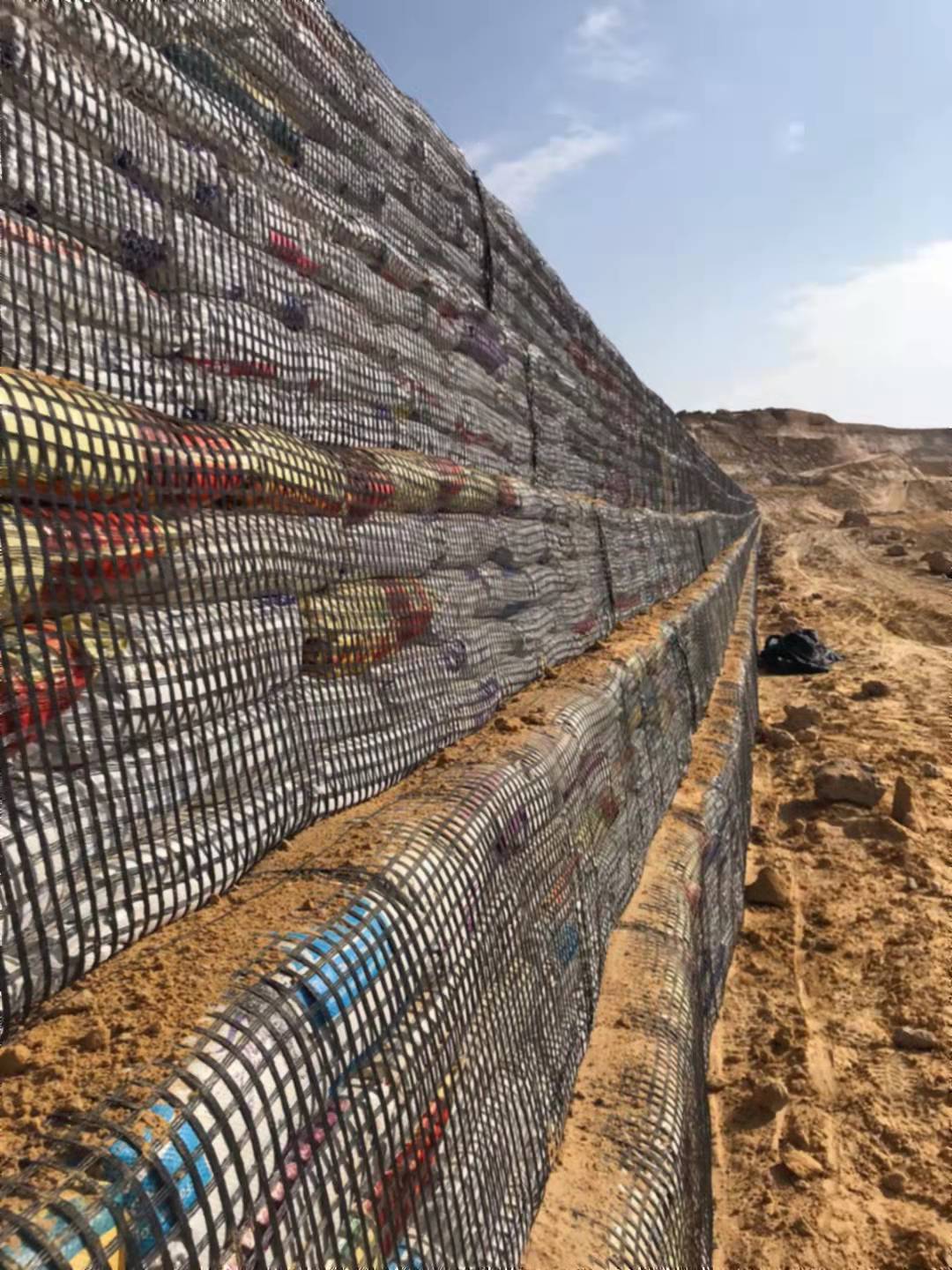
- Embankment Stabilization: Stabilizes slopes and embankments, preventing erosion and soil movement.
- Retaining Walls: Reinforces retaining structures, enhancing their load-bearing capacity and stability.
- Railway Construction: Supports railway tracks by distributing loads and reducing settlement, ensuring a smooth and stable track bed.
- Landfills: Reinforces landfill liners and caps, preventing waste migration and enhancing stability.
- Slope Protection: Protects against landslides and erosion in steep or unstable terrain.
Technical Specifications:
- Material: Extruded PET strips.
- Welding Method: Ultrasonic welding for strong and durable connections.
- Strength: High tensile strength with low elongation properties.
- Resistance: Chemical, UV, and biological resistance for long-term performance.
PET welded geogrids made from PET strips are a specialized type of geosynthetic material used for soil stabilization, reinforcement, and various civil engineering applications. Here’s an overview of the manufacturing process, quality control, and applications for PET welded geogrids made from PET strips:
Manufacturing Process of PET Welded Geogrids from PET Strips
- Material Selection:
- Polyester (PET) Strips: High-quality PET strips are selected for their superior tensile strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Strip Production:
- Extrusion: PET pellets are melted and extruded to form continuous strips.
- Orientation: The extruded strips are oriented to align the molecular structure, enhancing their tensile strength and reducing elongation.
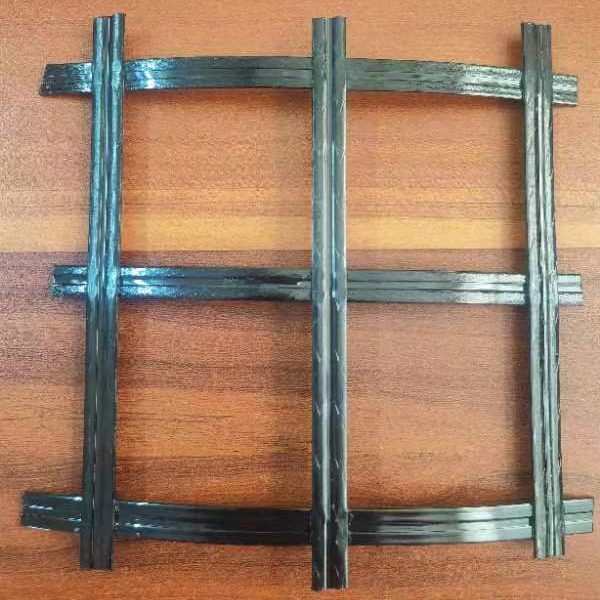
- Grid Formation:
- Strand Placement: The PET strips are arranged in a grid pattern, with precise spacing between the longitudinal (warp) and transverse (weft) strips.
- Welding: The intersections of the strips are welded together using thermal or ultrasonic welding techniques. This ensures strong bonds at the junctions, providing structural integrity to the geogrid.
- Coating Application:
- Protective Coating: A protective coating may be applied to enhance resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and biological degradation.
- Curing: The coated geogrid is cured to ensure proper adhesion of the coating.
- Cutting and Packaging:
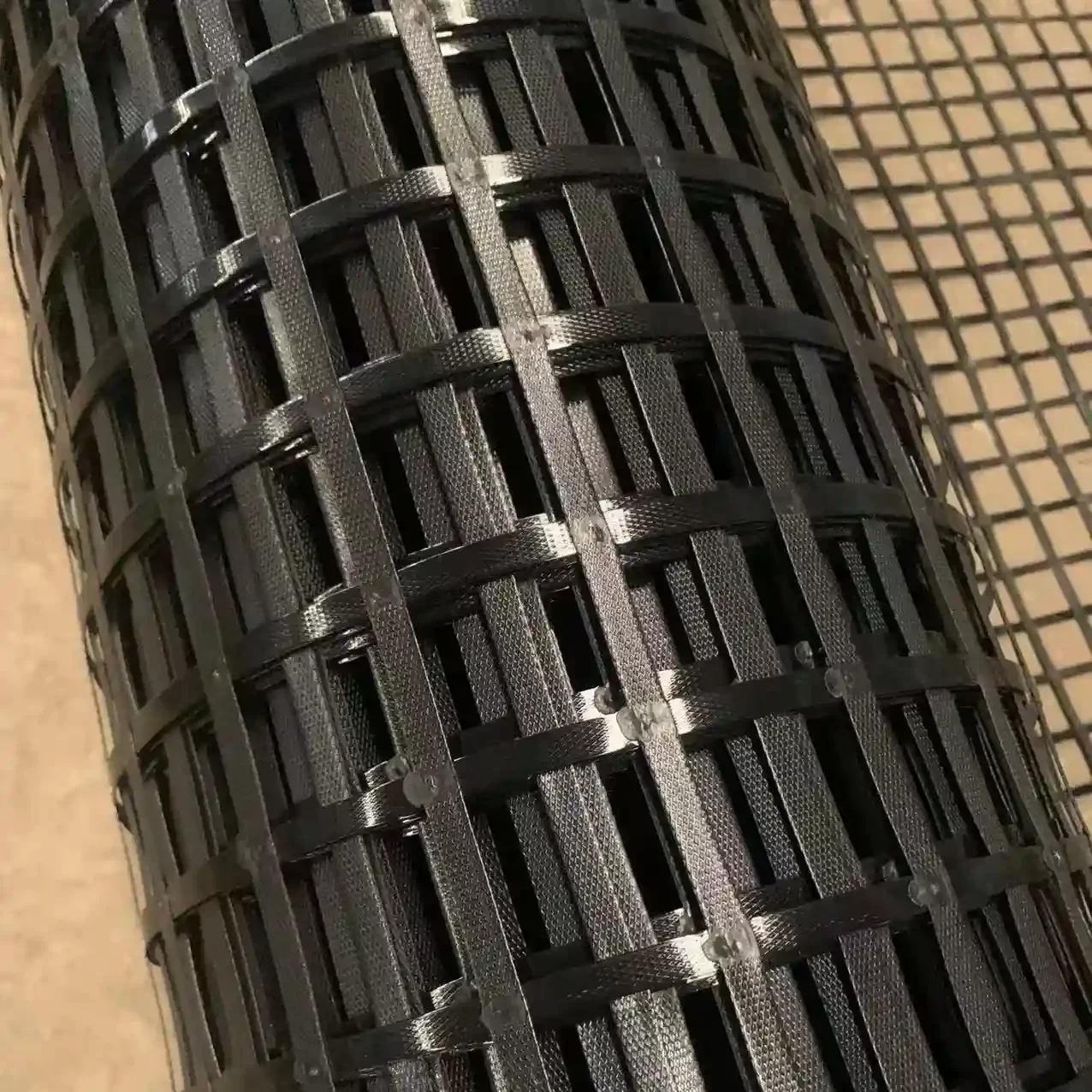
- Cutting: The welded geogrid is cut to the desired dimensions, typically in rolls of specified length and width.
- Packaging: The rolls are packaged to protect them during transportation and storage.
Quality Control Measures
- Raw Material Inspection:
- Material Testing: The PET strips and coatings are tested for quality, including tensile strength, elongation, and chemical resistance.
- Process Control:
- Monitoring: The extrusion, orientation, welding, and coating processes are closely monitored to ensure consistency and quality.
- Calibration: Equipment used in the manufacturing process is regularly calibrated to maintain precision.
- Product Testing:
- Tensile Strength: The tensile strength of the PET strips and the finished geogrid is tested to ensure they meet specifications.
- Weld Strength: The welds at the intersections are tested for strength to ensure they provide adequate structural integrity.
- Durability Testing: The geogrid undergoes tests for UV resistance, chemical resistance, and environmental durability.
- Dimensional Accuracy:
- Measurements: The dimensions of the geogrid, including strip spacing and overall width and length, are measured to ensure they meet specified tolerances.
- Visual Inspection:
- Defects: The finished geogrid is inspected for defects such as incomplete welds or coating inconsistencies.
- Uniformity: The uniformity of the grid pattern and coating application is checked.
- Certification and Documentation:
- Quality Certificates: Quality certificates documenting test results and inspections accompany each batch of geogrid.
- Traceability: Records are maintained for traceability of raw materials and the manufacturing process for each batch.
Applications of PET Welded Geogrids from PET Strips
- Soil Stabilization and Reinforcement:
- Road Construction: Used to reinforce subgrades and pavements, preventing rutting and extending the lifespan of roads.
- Railways: Reinforces track beds, ensuring stability and reducing maintenance costs.
- Slope and Embankment Stabilization:
- Erosion Control: Prevents soil erosion on slopes and embankments, enhancing stability and reducing sediment loss.
- Landslide Prevention: Provides reinforcement to prevent landslides and improve slope stability.
- Retaining Walls and Foundations:
- Structural Support: Reinforces retaining walls and foundations, preventing soil movement and enhancing structural integrity.
- Drainage: Ensures proper drainage behind retaining walls, reducing hydrostatic pressure.
- Mining and Tunneling:
- Ground Support: Provides stable ground support in mining and tunneling operations, enhancing safety and preventing collapses.
- Haul Roads: Reinforces haul roads, distributing loads from heavy equipment and reducing maintenance.
- Environmental and Hydraulic Applications:
- Landfills: Reinforces landfill liners and caps, preventing contamination and ensuring long-term stability.
- Water Management: Used in hydraulic structures to reinforce banks and prevent erosion.