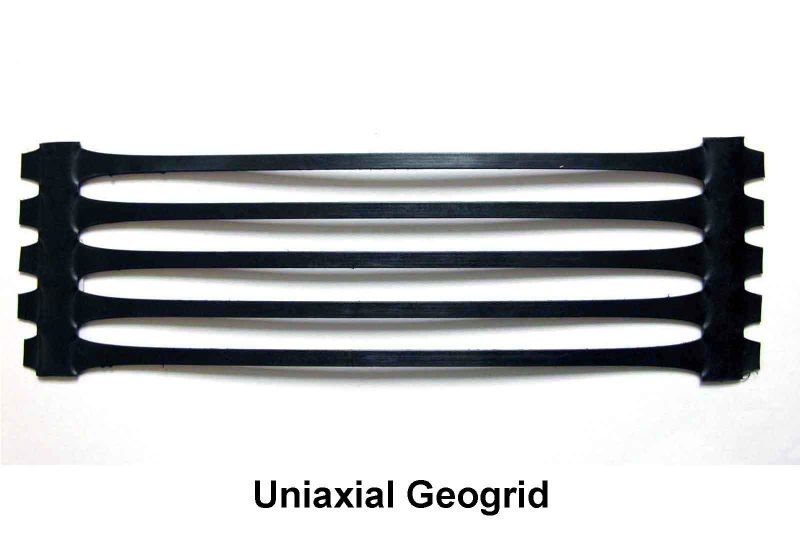
PP UNIAXIAL GEOGRID
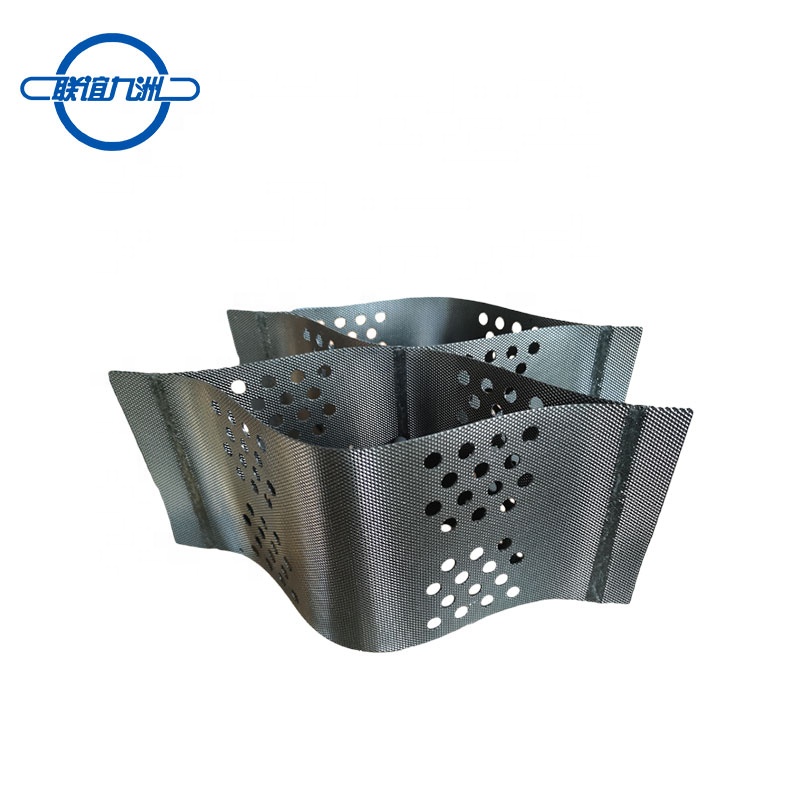
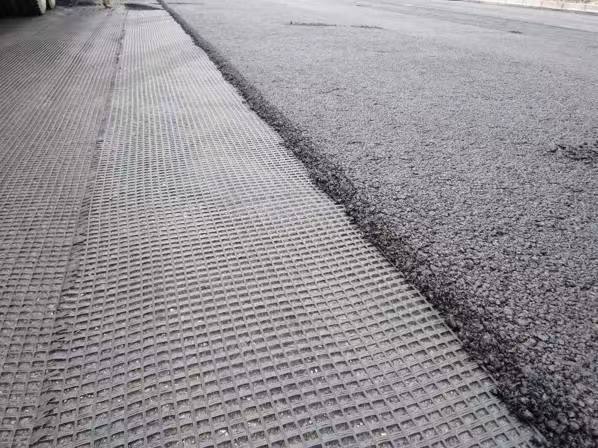
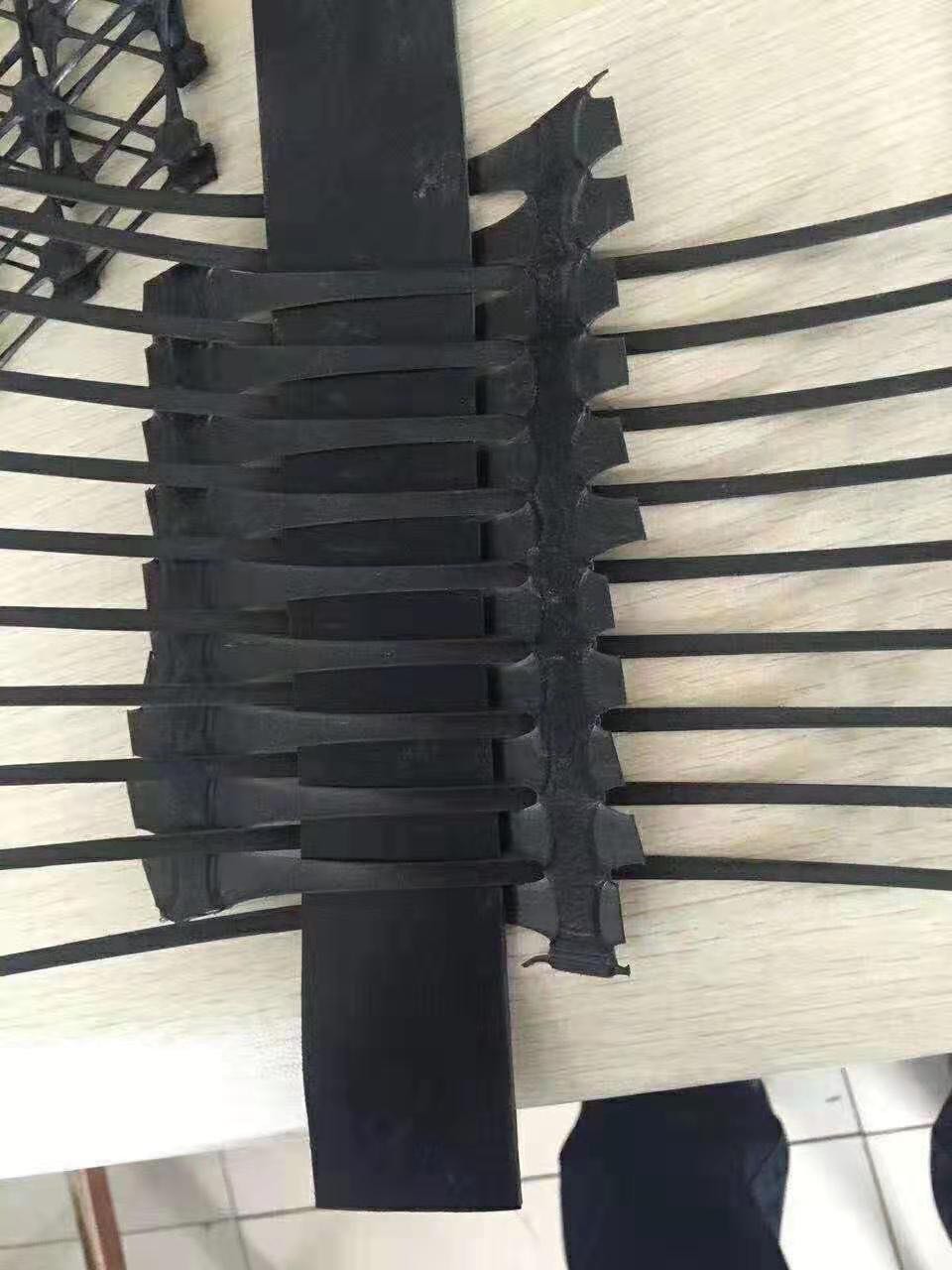
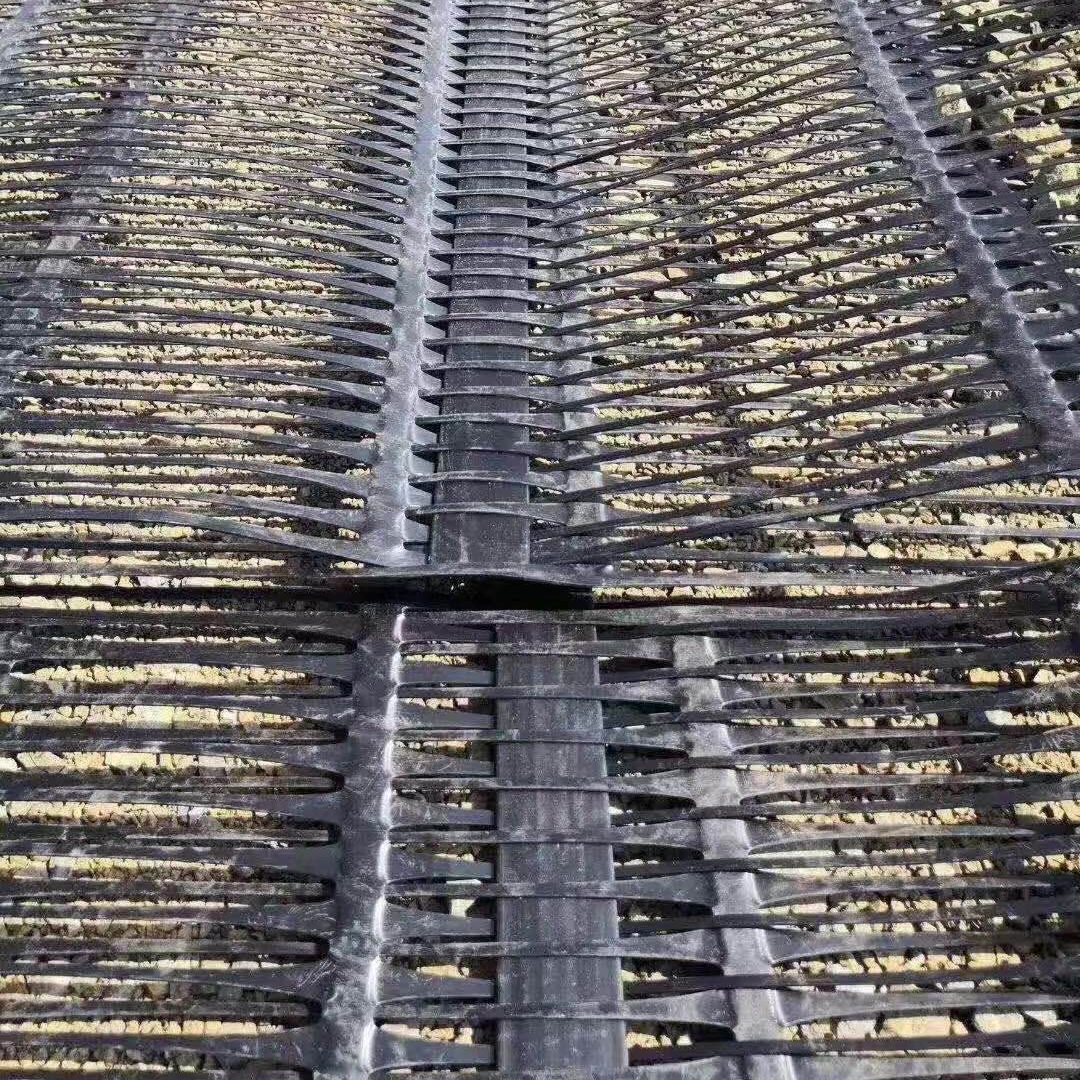
Polypropylene (PP) uniaxial geogrids are a type of geosynthetic material used in civil engineering and construction projects for soil reinforcement. Unlike biaxial geogrids, which provide strength in both directions, uniaxial geogrids are designed to provide high tensile strength primarily in one direction, making them ideal for applications where soil reinforcement is needed in a specific orientation.
Key Features of PP Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Material: Made from high-quality polypropylene, which offers excellent tensile strength and resistance to chemical and biological degradation.
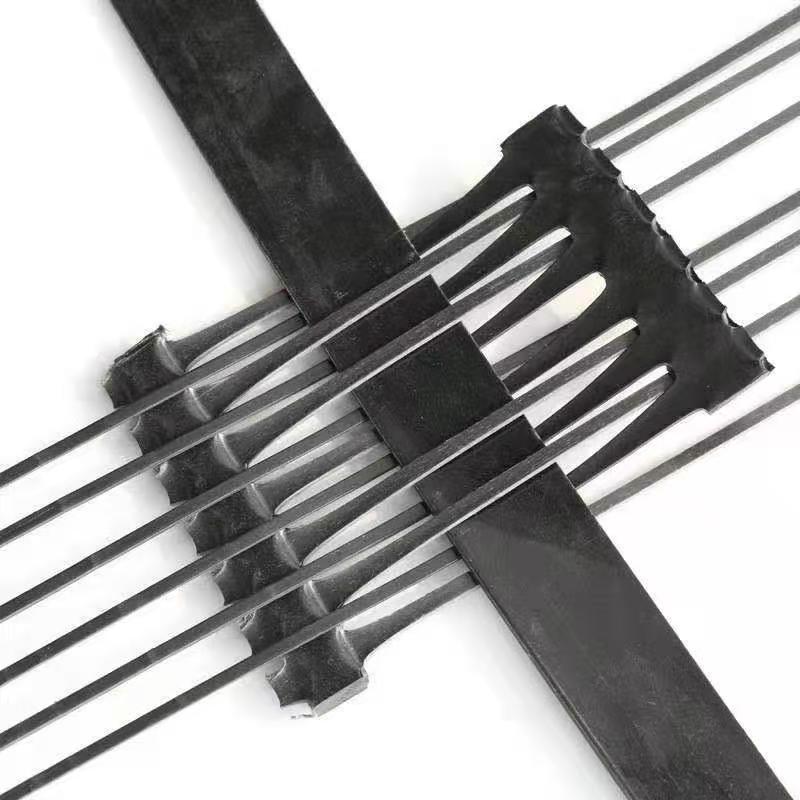
- Structure: The geogrid consists of a series of parallel ribs with perpendicular bars, creating an open grid-like structure that facilitates soil interaction.
- Directionality: Designed to provide maximum tensile strength in one direction, which is beneficial for reinforcing embankments, retaining walls, and other structures requiring unidirectional support.
- Durability: Resistant to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and microbial attack, ensuring long-term performance.
Lianyi’s PP (Polypropylene) uniaxial geogrid is an excellent choice for slope reinforcement due to its high tensile strength in one direction, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Here’s a detailed overview of why PP uniaxial geogrid is suitable for slope reinforcement, its benefits, installation process, and typical applications:
Why Choose PP Uniaxial Geogrid for Slope Reinforcement?
- High Tensile Strength:
- Provides exceptional tensile strength in one direction, which is critical for reinforcing slopes and preventing soil movement.
- Durability:
- Made from high-quality polypropylene, it is resistant to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and biological degradation, ensuring long-term performance even in harsh conditions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
- Flexible enough to conform to the slope’s contours while providing the necessary reinforcement.
- Cost-Effective:
- Reduces the need for extensive earthmoving and soil replacement, leading to cost savings in slope stabilization projects.
Benefits of Using PP Uniaxial Geogrid for Slope Reinforcement
- Enhanced Slope Stability:
- Prevents soil erosion and slope failure by reinforcing the soil and providing additional support.
- Load Distribution:
- Distributes loads evenly across the slope, reducing stress on any single point and minimizing the risk of slope failure.
- Improved Vegetation Growth:
- Facilitates vegetation growth on slopes by stabilizing the soil, which can further enhance slope stability and reduce erosion.
- Long-Term Performance:
- Withstands environmental challenges and maintains its structural integrity over time, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring long-term stability.
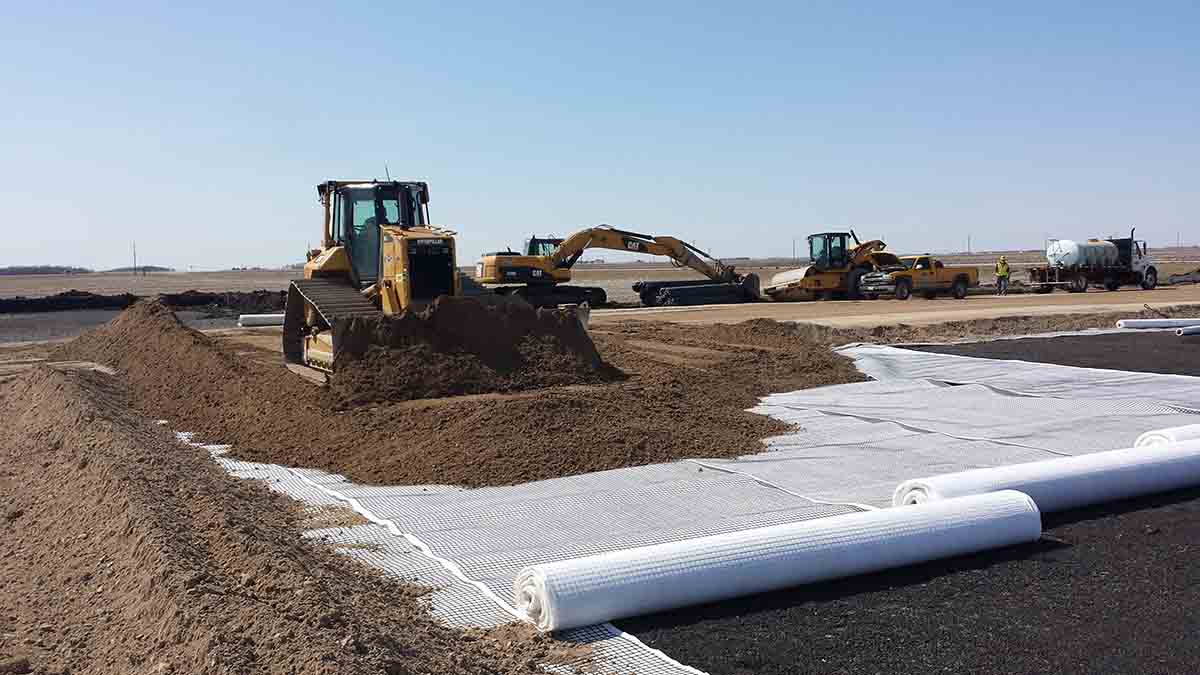
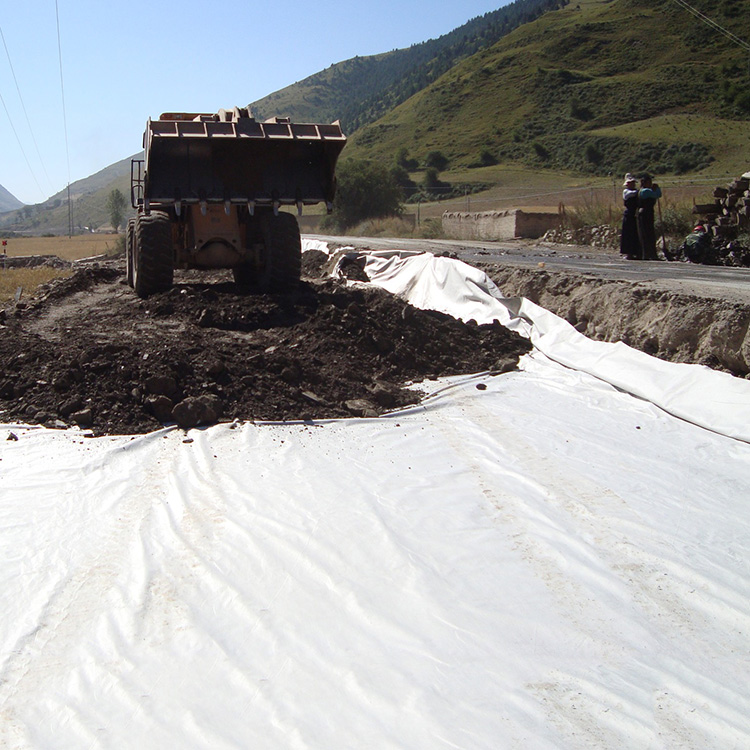
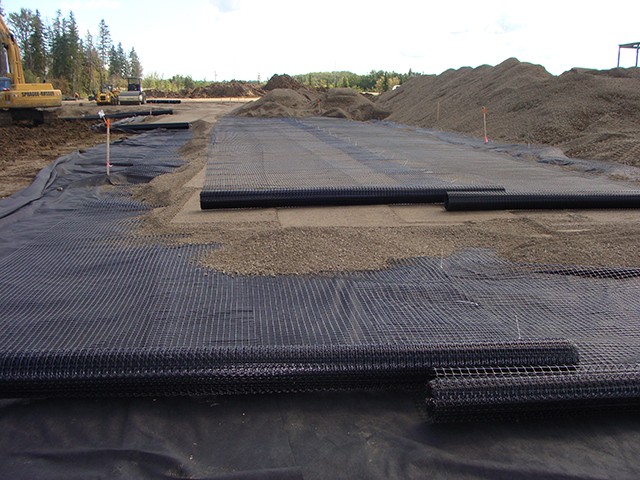
Installation Process
- Site Preparation:
- Clear the slope of any debris, vegetation, and loose soil. Ensure the slope is graded according to the design specifications.
- Geogrid Placement:
- Unroll the geogrid along the slope, ensuring it is properly aligned with the direction of the tensile strength. The geogrid should be anchored at the top and bottom of the slope.
- Anchoring:
- Secure the geogrid in place using ground anchors, stakes, or other suitable methods. Proper anchoring is essential to prevent movement during backfilling.
- Backfilling:
- Place and compact the fill material over the geogrid in layers. Ensure even distribution and compaction to avoid damaging the geogrid.
- Vegetation:
- If vegetation is part of the slope stabilization plan, apply topsoil and seed the slope to encourage plant growth, which will further stabilize the slope.
Manufacturing and quality control are critical aspects of producing high-quality PP (Polypropylene) uniaxial geogrids. Here’s a detailed overview of the manufacturing process and the quality control measures in place to ensure the product meets industry standards and customer requirements.
Manufacturing Process
- Raw Material Selection:
- Polypropylene Resin: High-quality polypropylene resin is sourced and tested to ensure it meets the required specifications for strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Additives: Stabilizers and UV inhibitors are added to enhance the geogrid’s resistance to degradation from UV radiation and chemical exposure.
- Extrusion:
- Extrusion Line: The polypropylene resin is fed into an extrusion line, where it is melted and extruded through a die to form a continuous sheet.
- Stretching: The extruded sheet is stretched in one direction (uniaxially) to align the polymer molecules, increasing the tensile strength in that direction.
- Punching and Drawing:
- Punching: The stretched sheet is then punched to create a regular pattern of apertures.
- Drawing: The punched sheet undergoes further drawing to refine the aperture size and shape, enhancing the geogrid’s mechanical properties.
- Cooling and Cutting:
- Cooling: The geogrid is cooled to stabilize its structure and dimensions.
- Cutting: The cooled geogrid is cut into rolls of specified widths and lengths.
- Winding:
- The finished geogrid is wound onto rolls, ready for packaging and shipment.