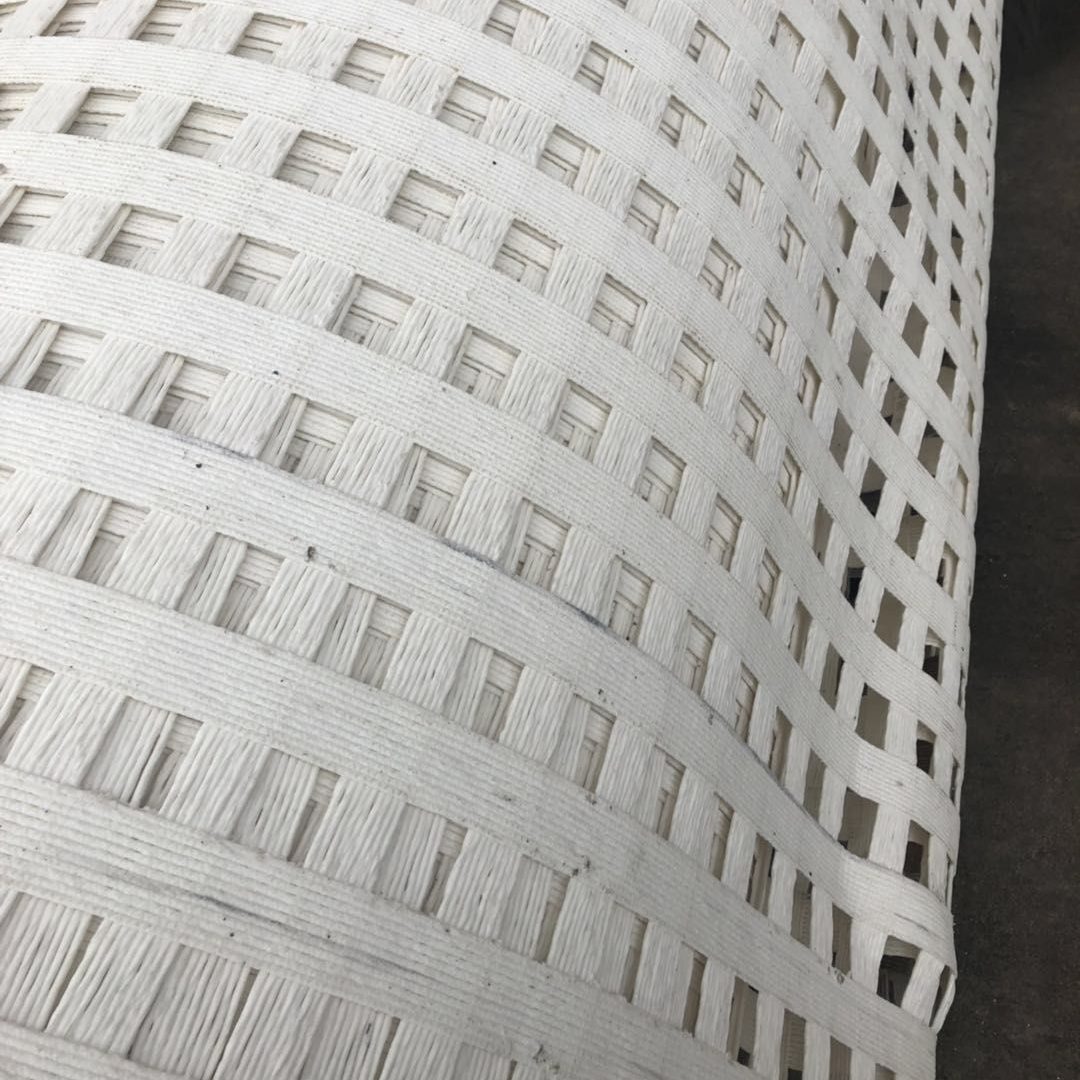
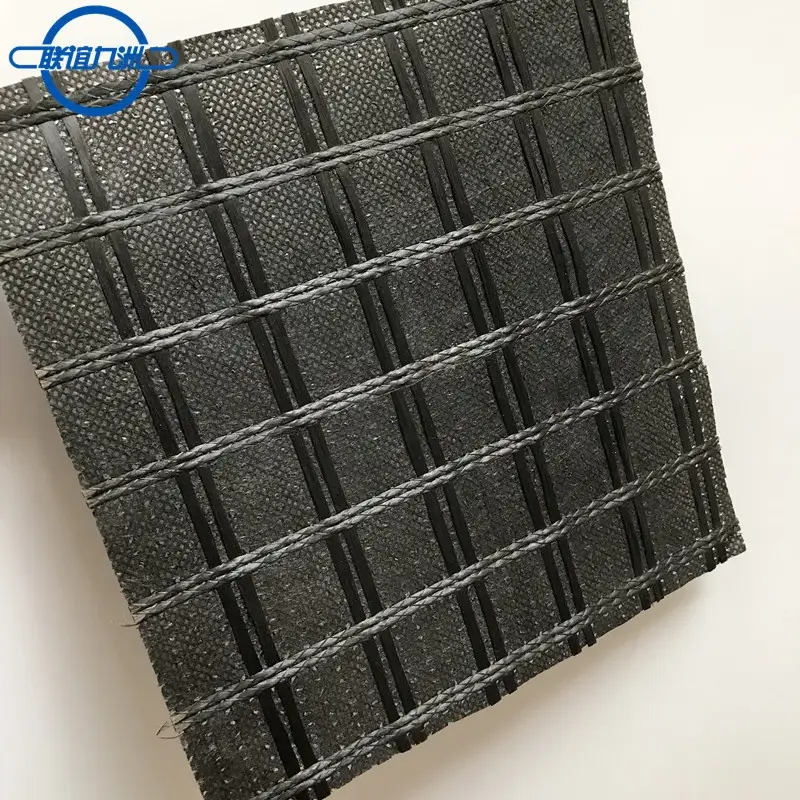
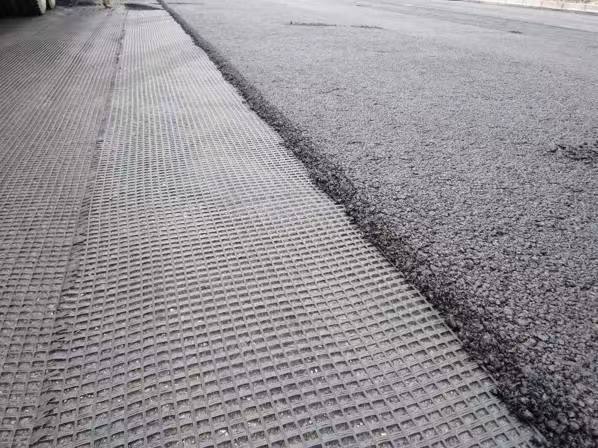
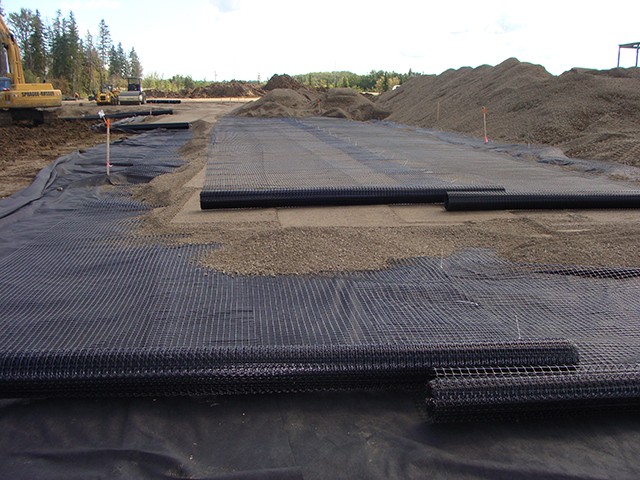
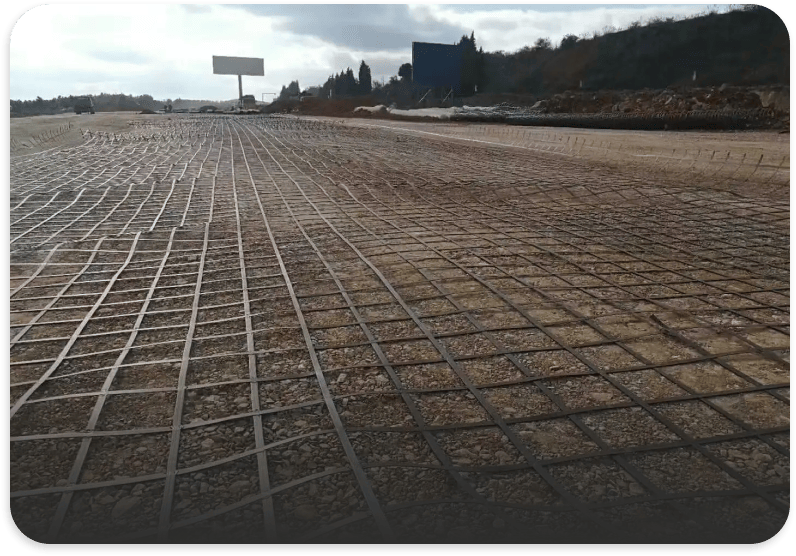
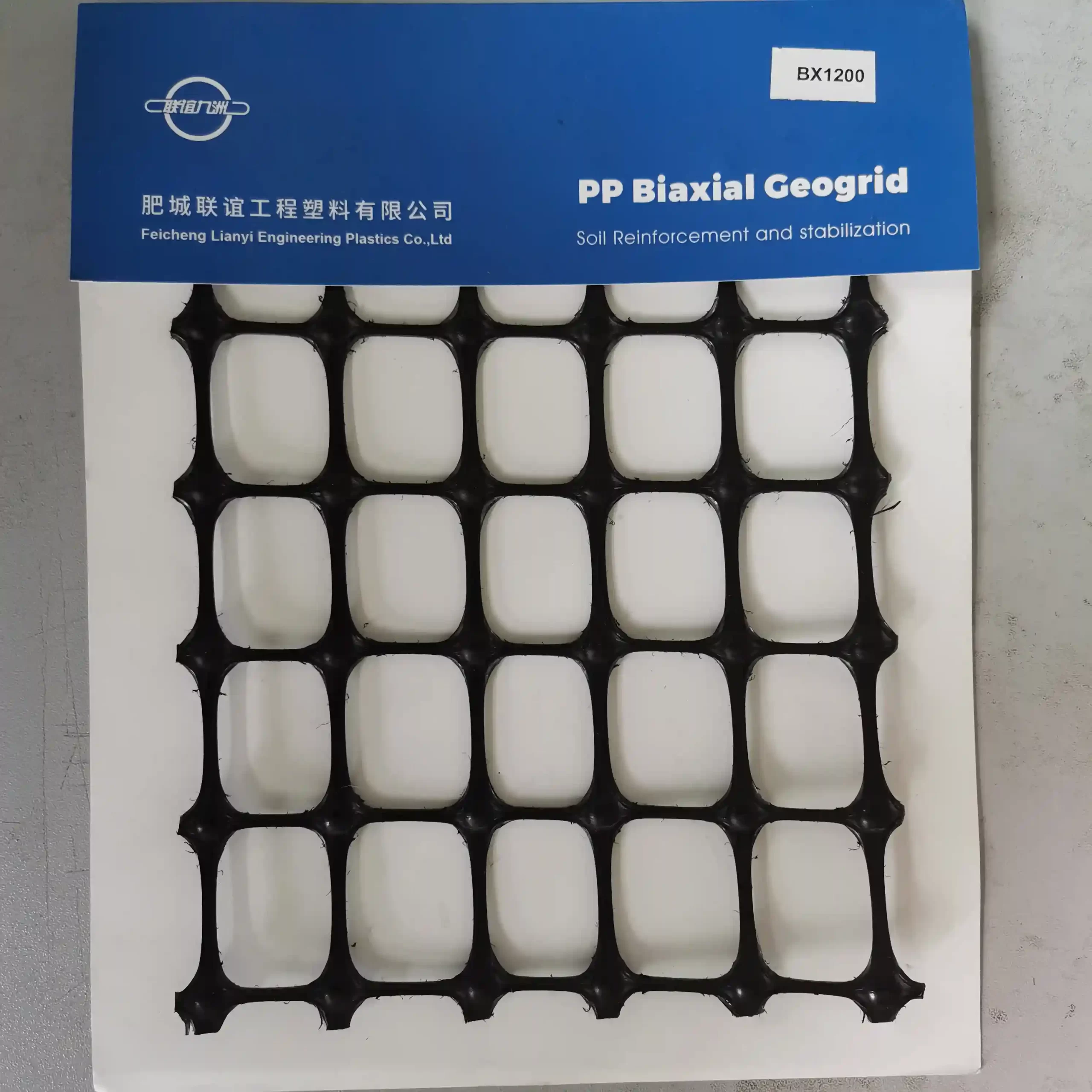
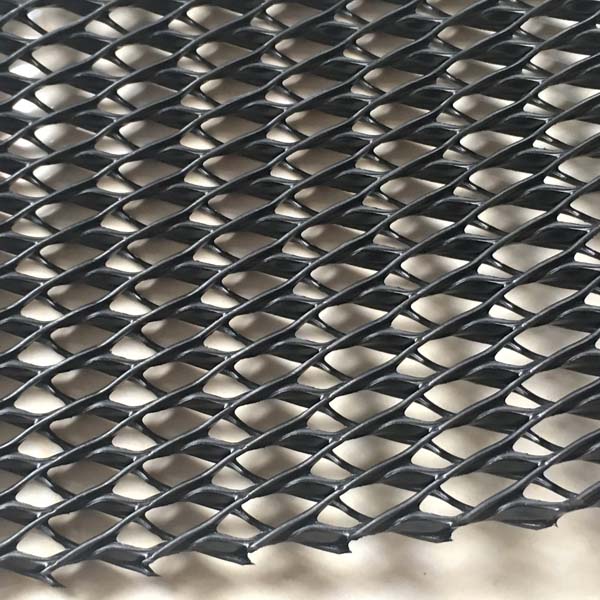
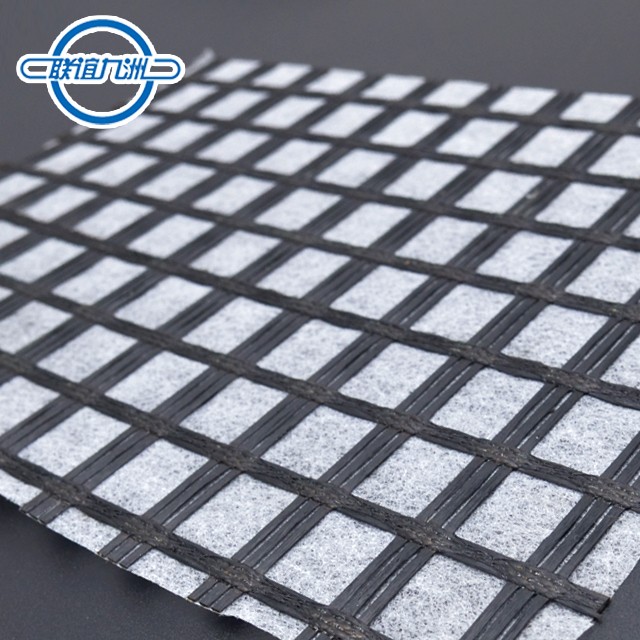
PP extruded geogrid BX1200 with rectangular mesh and biaxial geogrid with square mesh are two types of geosynthetic materials used for soil reinforcement and stabilization. Here are the key differences between them:
1. Mesh Shape and Size
Rectangular Mesh Geogrid:
- Aperture Shape: Rectangular
- Aperture Size: The length of the apertures is longer in one direction (machine direction or cross-machine direction) compared to the other.
- Load Distribution: Designed to provide different levels of stiffness and load distribution in the two directions due to the varying aperture sizes.
Square Mesh Geogrid:
- Aperture Shape: Square
- Aperture Size: The length and width of the apertures are equal, providing uniform grid openings in both directions.
- Load Distribution: Offers similar levels of stiffness and load distribution in both the machine direction (MD) and cross-machine direction (CMD).
2. Performance Characteristics
Rectangular Mesh Geogrid:
- Directional Strength: Typically provides higher tensile strength in one direction compared to the other. This makes it suitable for applications where directional load distribution is critical.
- Specific Applications: Often used in scenarios where the primary loads are expected to be more significant in one direction, such as in unidirectional load-bearing applications like certain types of embankments and roadways.
Square Mesh Geogrid:
- Balanced Strength: Provides similar tensile strength and stiffness in both directions, making it versatile for applications where loads are evenly distributed.
- General Applications: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including road construction, soil stabilization, retaining walls, and slope reinforcement, where balanced load distribution is required.
3. Design and Engineering Considerations
Rectangular Mesh Geogrid:
- Design Flexibility: Allows engineers to design reinforcement solutions tailored to specific directional load requirements.
- Installation Considerations: May require careful orientation during installation to ensure that the stronger direction aligns with the primary load direction.
Square Mesh Geogrid:
- Ease of Use: Simplifies installation as there is no need to orient the grid in a particular direction for optimal performance.
- Design Versatility: Suitable for general reinforcement purposes, providing a straightforward solution for various engineering challenges.
4. Typical Applications
Rectangular Mesh Geogrid:
- Roadway Construction: Particularly useful in reinforcing roads and highways where the primary stress is longitudinal.
- Railway Construction: Can be used in trackbed stabilization where directional load distribution is a key concern.
- Specific Slope Reinforcement: Applied in slopes and embankments where loads are predominantly in one direction.
Square Mesh Geogrid:
- General Soil Stabilization: Used in a wide range of soil stabilization projects, including roadways, parking lots, and foundations.
- Retaining Walls: Ideal for reinforcing soil behind retaining walls, providing balanced support.
- Erosion Control: Effective in preventing soil erosion in various environments, ensuring uniform reinforcement.
Summary
| Feature | Rectangular Mesh Geogrid | Square Mesh Geogrid |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture Shape | Rectangular | Square |
| Aperture Size | Longer in one direction | Equal in both directions |
| Load Distribution | Higher in one direction | Similar in both directions |
| Directional Strength | Uneven (higher in one direction) | Even (balanced in both directions) |
| Specific Applications | Directional load-bearing scenarios | General load distribution scenarios |
| Installation Considerations | Orientation required | No specific orientation needed |
| Typical Applications | Roads, railways, specific slopes | General stabilization, retaining walls, erosion control |
The performance of the PP extruded geogrid BX1200 is characterized by several key factors that make it an effective solution for soil reinforcement and stabilization in civil engineering and construction projects. Here’s a detailed look at its performance attributes:
1. Tensile Strength
- High Tensile Strength: BX1200 provides significant tensile strength in both the machine direction (MD) and the cross-machine direction (CMD). This strength allows it to effectively distribute loads and reinforce the soil.
- Ultimate Tensile Strength: Typically around 20-30 kN/m for both MD and CMD.
- Tensile Strength at 2% and 5% Strain: The grid maintains substantial tensile strength at low strains, providing immediate support under loads.
2. Load Distribution
- Effective Load Distribution: The grid’s structure distributes loads more evenly across the soil, reducing stress concentrations and preventing deformation. This is especially important for applications like road and pavement construction, where even load distribution extends the lifespan of the surface.
3. Soil Reinforcement
- Enhanced Soil Stability: BX1200 reinforces the soil, increasing its shear strength and reducing the risk of soil movement or failure. This makes it ideal for applications such as retaining walls, slopes, and embankments.
4. Durability
- Chemical and Biological Resistance: The polypropylene material is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts. It is also resistant to biological degradation, including from fungi, bacteria, and insects.
- UV Resistance: High resistance to UV degradation ensures long-term performance even when exposed to sunlight.
- Temperature Range: BX1200 remains effective in a wide range of temperatures, typically from -30°C to +70°C, making it suitable for various climatic conditions.