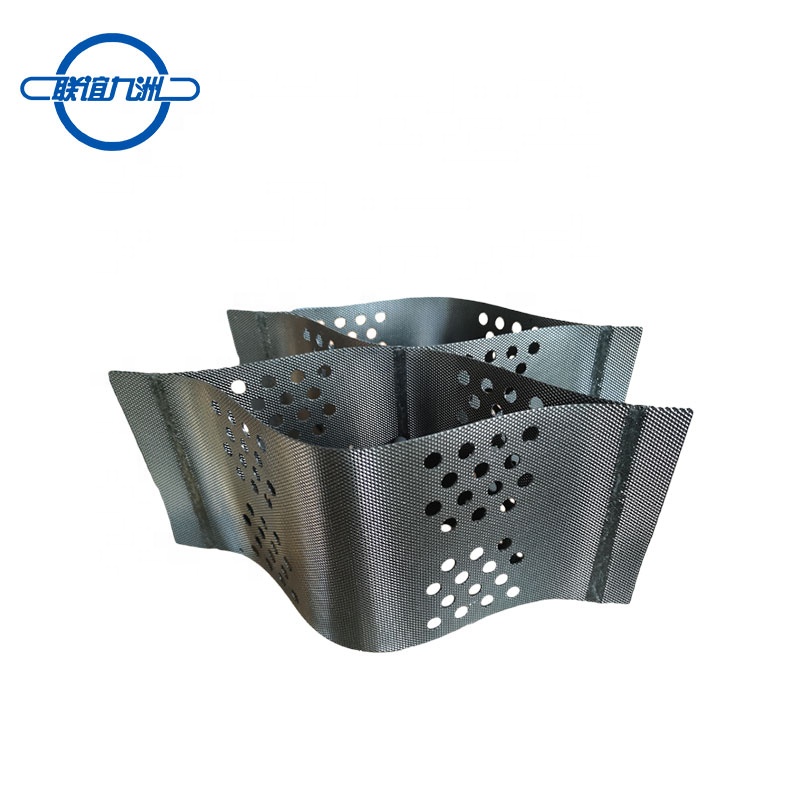
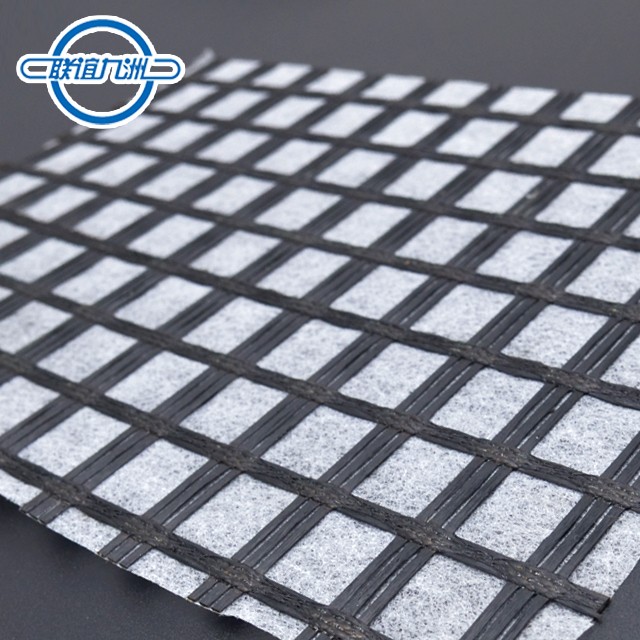
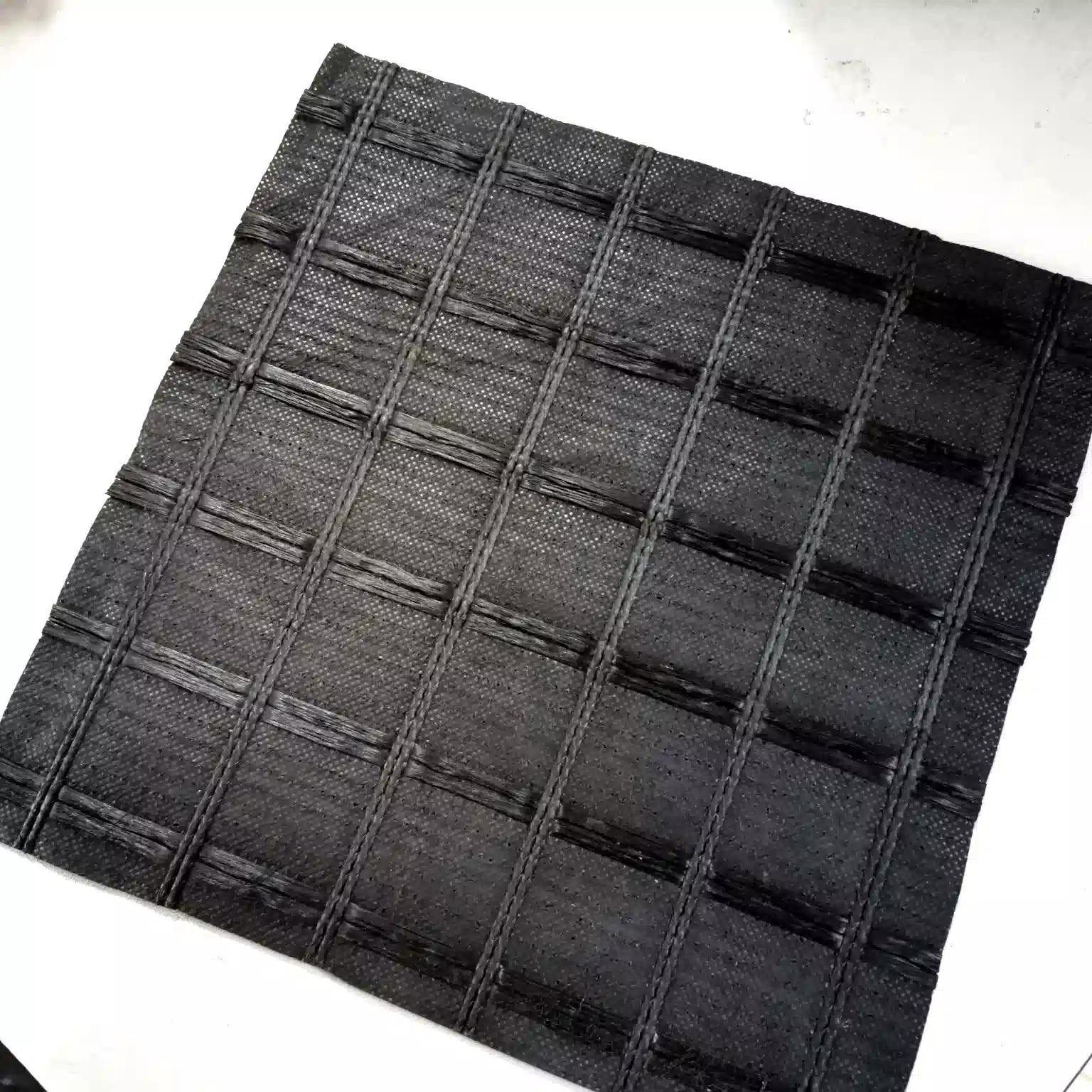
Lianyi steel-plastic composite geogrids are advanced materials used in road construction to enhance the performance and longevity of roadways. These geogrids combine the high tensile strength of steel with the durability and flexibility of plastic, creating a robust reinforcement solution. Here’s a detailed look at their features, applications, and benefits:
Key Features of Steel-Plastic Composite Geogrids
High Tensile Strength: The integration of steel wires within the plastic matrix provides exceptional tensile strength, making these geogrids highly effective in reinforcing road structures.
Durability and Flexibility: The HDPE(or LDPE) sheath imparts flexibility and resistance to environmental factors, such as UV radiation, chemicals, and moisture.
Dimensional Stability: The composite structure ensures dimensional stability under varying loads and temperatures, which is crucial for maintaining road integrity.
Resistance to Creep: Steel-plastic geogrids exhibit low creep, meaning they can withstand prolonged loading without significant deformation.
Improved Load Distribution: The grid structure helps in distributing loads evenly across the road surface, reducing stress on the subgrade and preventing pavement failures.
Applications in Road Construction
Base and Sub-base Reinforcement: Used to reinforce the base and sub-base layers of roads, improving their load-bearing capacity and durability.
Soft Soil Stabilization: Effective in stabilizing soft or weak soils, preventing excessive settlement and enhancing the overall stability of the road structure.
Pavement Reinforcement: Used in both flexible and rigid pavements to prevent reflective cracking and rutting, thereby extending the pavement life.
Embankment and Slope Stabilization: Provides reinforcement for embankments and slopes adjacent to roadways, reducing the risk of landslides and soil erosion.
Railway Construction: Also applicable in railway track reinforcement, where high tensile strength and stability are required to support heavy loads.
Installation Process
Site Preparation: The construction site is cleared and graded to the required specifications.
Laying the Geogrid: The steel-plastic composite geogrid is unrolled over the prepared surface. It can be cut to fit specific areas as needed.
Anchoring: The geogrid is anchored in place using pins or other suitable methods to ensure it remains stationary during the construction process.
Backfilling: Aggregate or soil is placed over the geogrid. The material is typically compacted in layers to achieve the desired thickness and density.
Overlaying: Additional layers of geogrid may be applied if required, followed by further backfilling and compaction until the road structure is complete.